
Category: Tech
Haribo made the best smartphone power bank. Then the dangerous defects emerged.
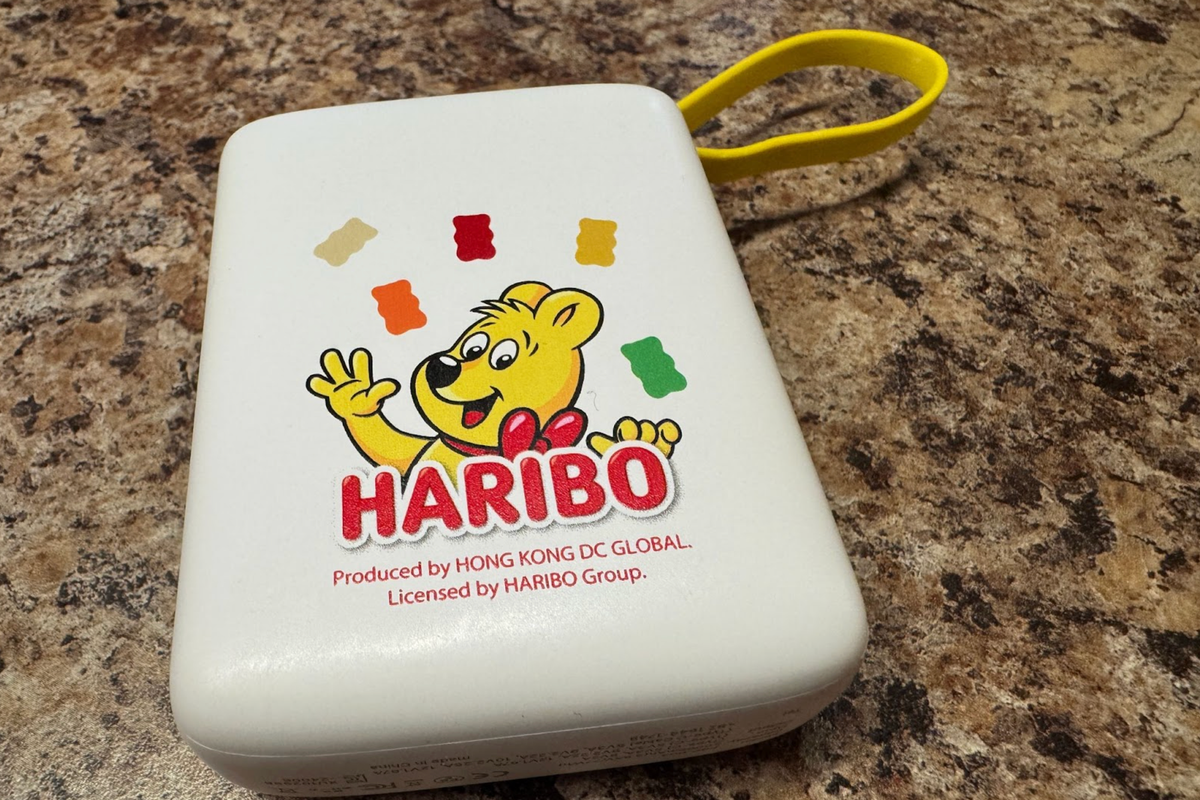

You know the old saying: If it’s too good to be true, then it probably is. You know Haribo, the gummy bear brand? It turns out that the company also sells gummy bear-themed electronics, and its power banks went viral this year for delivering an absurd amount of battery life in a cheap, lightweight package. Backpackers especially loved them because they were so lightweight, and I bought one to try it for myself. But as you can guess, it turned out to be too good to be true.
The Haribo 20,000mAh power bank showed up on Amazon sometime in early 2025, made by a Hong Kong company called DC Global and licensed under the Haribo brand. It had three things going for it: It was light (286 grams), it was cheap ($22-$25), and it had a little fake gummy bear dangling off the USB-C cable.
Ultralight backpackers lost their minds. For years, the gold standard had been Nitecore batteries that weighed significantly more and cost five times as much. The Haribo undercut them both on weight and price while supposedly matching their specs. Reviews poured in praising the thing. I read several before buying mine, and they all said the same thing: This is too good to be true, but it actually works.
Then Amazon suddenly pulled them in November for unspecified safety issues. Two weeks later, CT scans revealed what the problem likely was: dangerous defects.
Structural defects increase the risk of thermal runaway, the technical term for when a battery decides to become a flamethrower.
Meanwhile, I’m still here, and my bag hasn’t burst into flames. The thing works exactly as advertised. Which doesn’t mean the concerns aren’t real, but it does mean we need to talk about what’s actually happening here, not just what the headlines say.
What the CT scans actually show
Jon Bruner at Lumafield published his findings in late November, and they’re not good. The battery cells inside the Haribo power bank show misaligned electrodes. In other words, the layers that should stack neatly are instead wavy, bulging, and shifted. In lithium-ion batteries, this kind of manufacturing sloppiness creates conditions for lithium plating and dendrite growth, which can eventually lead to internal shorts. Internal shorts mean fires.
The scans also revealed irregular geometry and poor edge alignment, suggesting weak quality control throughout the manufacturing process. These aren’t minor cosmetic issues. These are structural defects that increase the risk of thermal runaway, which is the technical term for when a battery decides to become a flamethrower.
Bruner’s post went viral: 4.4 million views on X. Amazon quietly canceled existing orders and pulled the listings, citing “potential safety or quality issues.” No official government recall, just a quiet removal.
The problem with ‘dangerous’
So here’s where it gets complicated. Is the Haribo power bank dangerous? Yes, in the sense that it has manufacturing defects that increase risk. But how dangerous? That’s harder to say.
Lithium-ion batteries fail all the time. Samsung had to recall millions of Galaxy Note 7 phones in 2016. Anker recalled over a million PowerCore 10000 units just this year. Belkin, ESR, and half a dozen other companies have pulled products for overheating risks. The CPSC recalls portable batteries practically every month. It’s not unique to Haribo, and it’s not unique to cheap batteries.
The truth is that most defective batteries never catch fire. They degrade faster, lose capacity, or just stop working. The fires are rare but catastrophic, which is why we treat them seriously. But “rare but catastrophic” doesn’t mean every unit is a ticking time bomb.
The other ugly truth is that these high-capacity lithium-ion batteries are small bombs in disguise.
RELATED: Here’s how to get the most annoying new update off of your iPhone
 Photo by: Nano Calvo/VW Pics/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
Photo by: Nano Calvo/VW Pics/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
And eventually, they all go bad. Leave a laptop sitting for long enough, and the battery will swell. iPhones catch on fire all the time. But usually, they don’t, and the small risk is something that we as a society have decided to accept.
I have been using my Haribo battery for months. It has charged my phone maybe 50 times. It has been in my truck, in my backpack, sitting on my desk. No heat. No swelling. No weird behavior. Does that prove it is safe? No. Does it mean I’m an idiot for still using it? Maybe. But it does mean that the risk isn’t as immediate as the headlines suggest.
The real problem: Trust and transparency
The bigger issue here isn’t just the Haribo power bank. It’s that we have no way of knowing which products are actually safe and which ones are cutting corners until something goes wrong.
DC Global, the Hong Kong manufacturer behind the Haribo, won’t tell you what’s inside its batteries. Neither will most companies. You’re buying on faith — faith in brand reputation, faith in Amazon’s vetting, faith that someone, somewhere is checking these things. And that faith is often misplaced.
Amazon pulled the Haribo on November 12, citing vague “safety or quality” concerns but offering no specifics. Two weeks later, Lumafield published its CT scan investigation, revealing exactly what those concerns likely were. We still don’t know what tipped Amazon off in the first place. Customer complaints? Internal testing? We’re left guessing.
What we do know is that it took an independent company with expensive CT scanning equipment to show the public what was actually hiding inside a plastic shell with a gummy bear on it. Without Lumafield’s investigation, we would still be in the dark about why these disappeared.
How many other products have similar issues that we just don’t know about yet?
What you should actually do
If you own a Haribo power bank, should you get rid of it?
That’s up to you. I’m still using mine, but I’m watching it. I’m not leaving it charging overnight. I’m not throwing it loose in a bag with other batteries. I’m treating it like what it is: a cheap Chinese import with questionable quality control.
If you do decide to dispose of it, don’t just toss it in the trash. Lithium-ion batteries are hazardous waste and can cause fires in garbage trucks and landfills. Take it to a proper recycling center — places like Home Depot, Best Buy, and other retailers have Call2Recycle drop-off locations. Discharge it fully first, tape over the terminals with electrical tape, and put it in a plastic bag. You can find a location near you at call2recycle.org/locator.
Should you buy one? No. It has been pulled from Amazon anyway. But even if it comes back or you find one on eBay, don’t. Not because it is guaranteed to explode, but because the uncertainty isn’t worth it.
Are there perfect alternatives? No. Anker just recalled over a million units. Nitecore costs five times as much. Every lithium-ion battery carries some risk. But at least with established brands, there is a recall process. There is accountability. There is someone to contact when things go wrong.
With the Haribo, you get none of that. Just a disappeared Amazon listing and a manufacturer that has gone silent.
The Haribo was appealing because it was cheap, light, kind of funny. But cheap comes with costs you can’t always see until someone with a CT scanner shows you.
A cautionary tale
The Haribo power-bank story is a perfect example of how modern consumer products work. A company in Hong Kong slaps a candy brand on a battery, ships it through Amazon, gets praised by reviewers, goes viral on social media, and then quietly disappears when something raises red flags.
No accountability. No transparency. No consequences. Just a listing that vanishes and thousands of units still sitting in people’s bags.
Amazon knew enough to pull it but won’t say why. Lumafield’s scans showed us the structural problems, but only after the fact. There is no official recall, no manufacturer statement, no clear guidance for the people who bought these things in good faith — just a void where answers should be.
The regulatory system should not ban everything that poses a risk. But we deserve to know what we’re buying. We deserve manufacturing standards that mean something. We deserve companies that don’t hide behind licensing deals and overseas production to dodge responsibility. And we deserve regulatory agencies that can move faster than a thread on X.
Tech CEOs Detail U.S. Investment Commitments During Roundtable with Trump
WASHINGTON–Tech CEOs joined President Donald Trump at the White House on Wednesday, where they shared their investment commitments over the coming years.
The post Tech CEOs Detail U.S. Investment Commitments During Roundtable with Trump appeared first on Breitbart.
This new malware wants to drain your bank account for the holidays. Here’s how to stay safe.

Android security has come a long way since the early days, thanks largely to Google’s broad suite of virus-busting tools, like Play Protect for apps, Safe Browsing for the web, and the Advanced Protection Program for Google accounts. However, malware can still infect devices from time to time, and the latest threat aims to infiltrate your bank account just before the holidays.
The threat
Dubbed Sturnus, this latest Android threat is a classic Trojan horse malware that bypasses Android’s security protections to gain access to a target device. Once inside, a hacker can spy on your conversations in popular chat apps — like Signal, Telegram, and WhatsApp — and even mimic your bank’s login screen to trick you into handing over your bank login and password.
What makes this malware especially tricky lies in its sophistication. Sturnus doesn’t break the encryption found in the popular apps listed above. Instead it exploits Android’s native accessibility features to view, detect, and record data shown on your screen. The malware even comes with uninstall protection, making it harder to remove from a device once infected.
Here are some things you can do to make sure your Android phone is protected from Sturnus.
How to know if your phone is infected with Sturnus
Sturnus is especially dangerous because it runs completely undetected. There’s currently no way to know for sure that the malware is installed on your device. It could be lurking in your phone right now!
But don’t panic just yet. You’re less likely to be infected if either of these apply to you:
First, Sturnus is only transmitted through downloading and installing an Android app (an APK file, also known as an Android Application Package) directly to your phone. More than that, the infected APK file has to come from a third-party source outside of the Google Play Store — either in an attachment sent through a spam message or via a third-party app store. In a statement provided to Android Authority, Google confirmed that all Android users who strictly download apps from the Google Play Store are safe:
Based on our current detection, no apps containing this malware are found on Google Play. Android users are automatically protected against known versions of this malware by Google Play Protect, which is on by default on Android devices with Google Play Services. Google Play Protect can warn users or block apps known to exhibit malicious behavior, even when those apps come from sources outside of Play.
Second, Sturnus has only been detected in devices based in South and Central Europe so far. Users in the United States aren’t under any direct threat right now, but this could change as we get further into the holidays.
How to prevent Sturnus from infecting your phone
Just to be safe, there are some things you can do to make sure your Android phone is protected from Sturnus or any other downloadable security threat.
Google Play Protect
Make sure Google Play Protect is on. This feature regularly scans the apps downloaded to your phone and checks them for “harmful behavior,” including viruses and malware. To enable Play Protect, open the Google Play Store app on your phone, tap your profile picture in the top right corner, then Play Protect. Make sure it’s turned on.
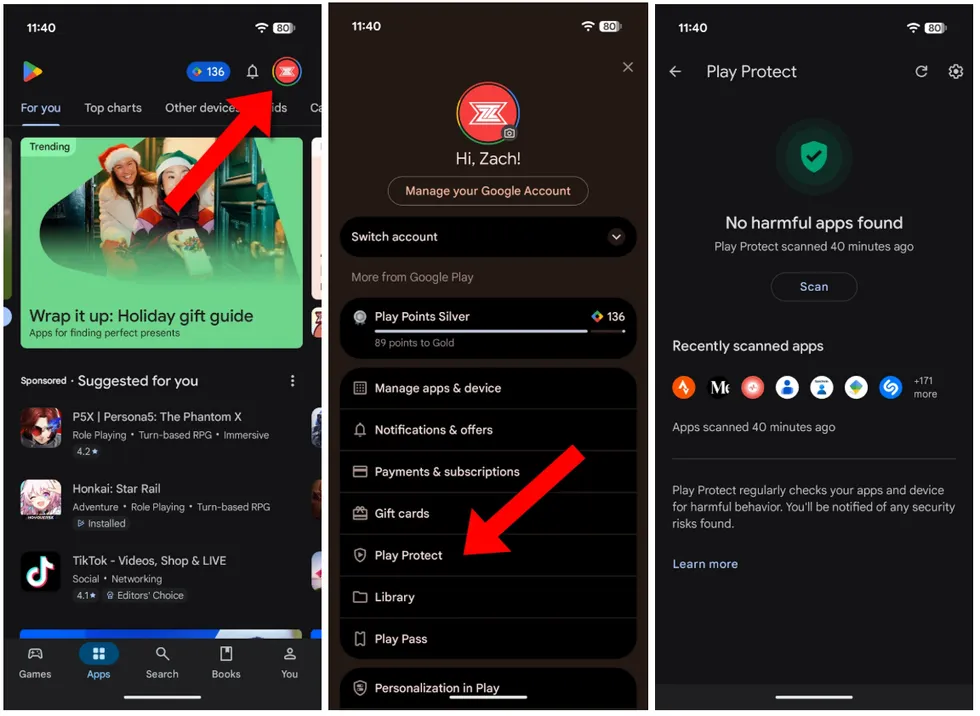 Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
Disable ‘Install unknown apps’
The Google Play Store is the default app store found on most Android devices sold in the U.S. Although Android phones can download apps from other sources, most of them ship with this feature turned off by default. Still with Sturnus going around, it’s a good idea to check to make sure your phone can’t accidentally sideload an app from a dubious corner of the internet.
If you have a Samsung Galaxy phone, open the Settings app, tap on “Security and privacy,” then “More security settings,” and finally “Install unknown apps.” Make sure every app on this page is unchecked.
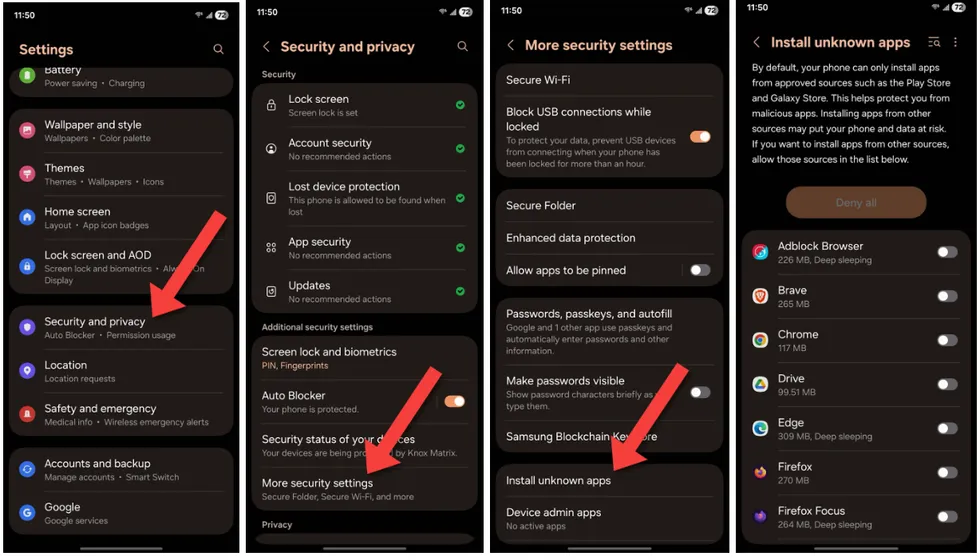 Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
If you have a Google Pixel phone, open the Settings app, tap on “Apps,” then “Special app access,” and lastly “Install unknown apps.” As with Samsung, make sure every app on this page is disabled.
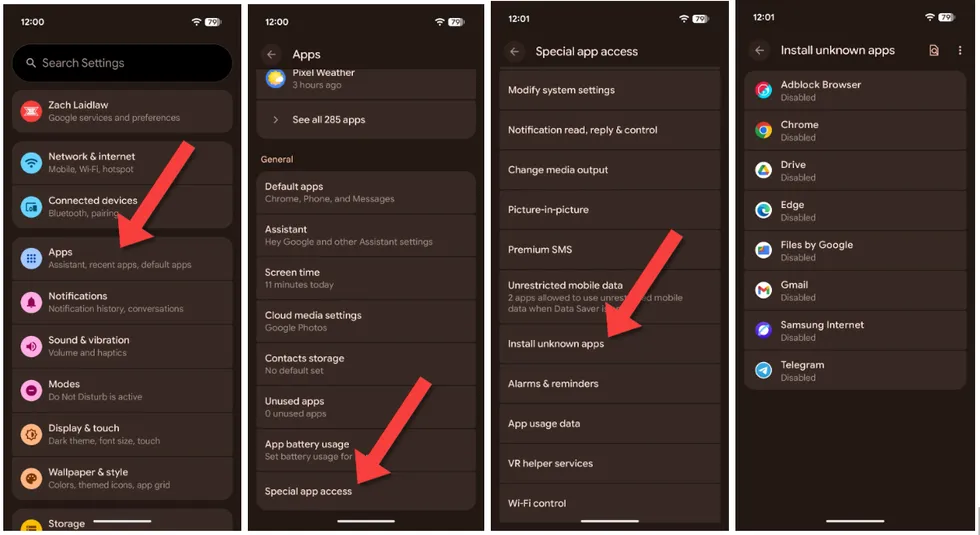 Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
Screenshots by Zach Laidlaw
For those with other-branded Androids, you should be able to find this feature by opening your Settings app and typing “install unknown apps” into the search bar. As with the devices above, make sure this feature is disabled.
Extra features
Depending on your device, some Android phones come with additional security features that protect against malware, both on the software side and the hardware side. For instance, Samsung Knox protects data and defends from cybersecurity threats. As for Pixels 6 and up, they come with a Titan M2 chip that makes it harder for hackers to access your phone if it’s stolen, plus regular monthly security updates directly from Google ensure that their phones are always up to date.
The fix?
At this time, there is currently no fix for Sturnus, and there isn’t likely to be one anytime soon. Since the malware exploits several important features baked directly into the Android operating system, Google would have to disable these features entirely to get rid of the problem, something that simply can’t be done.
RELATED: Cloudflare crash exposes the internet’s fragile core — and worse may be coming
 Photo by Jakub Porzycki/NurPhoto via Getty Images
Photo by Jakub Porzycki/NurPhoto via Getty Images
With Sturnus on the rise, it’s probably not a coincidence that Google recently announced that it is making it more difficult to distribute and sideload unverified apps from third-party sources. The move would prevent this exact kind of malware from infecting devices worldwide, though backlash from avid Android users has caused Google to loosen these restrictions just a bit. The final version of the sideloading changes are expected to roll out starting in late 2026.
As for now, your best bet to keep Sturnus out of your phone is to stay away from APKs that come from anywhere outside of the Google Play Store. Do that one simple thing, and you have nothing to worry about.
Can this high-stakes overhaul save Ethereum from the dustbin of crypto?

It was once fashionable to speak of Ethereum as a “world computer,” a phrase that suggested a certain noisy, industrial utilitarianism. The idea was that every instruction, every transfer of value, every digital breath would be executed publicly and redundantly by a global network of nodes, a process that was transparent, unstoppable, and, as it turned out, prohibitively slow.
Although Ethereum in 2015 aimed at radical transparency, it is now engaged in a great transformation, an architectural renovation carried out while the building is still occupied. Ethereum is remaking itself not with more computing power, but with the mathematics of shadows: zero-knowledge proofs.
Ethereum replaces personal trust with mathematical guarantees, accountability without surveillance.
The central tension of the digital age has always been this trilemma: how to remain secure and decentralized while scaling to meet a global demand. Ethereum’s answer is to turn to an innovation in cryptography: the zero-knowledge proof, a protocol that allows one party to prove a statement is true without revealing why it is true, or indeed revealing any other information at all. It is a way to convince a stranger that you know a secret without ever telling him the secret itself. This property, which borders on the magical, is being woven into the very foundations of the network.
The heavy lifting of transaction execution is leaving the main stage. The Ethereum roadmap, in a phase titled the “Surge,” dictates that most activity will now occur off-chain, on Layer-2 networks known as rollups. These rollups bundle thousands of transactions, execute them in the dark, and generate a succinct validity proof, which is then posted back to Ethereum’s main layer. The main chain, once the sweating engine of the network, is now a high-security court, a judge that need not hear the testimony, only see the irrefutable mathematical certificate of the verdict.
Instead of a world computer, Ethereum is becoming a “world settlement layer,” an anchor for off-chain environments. To facilitate this, the network has introduced “blobs,” an inelegantly named but vital innovation of the Dencun upgrade. Blobs are temporary data, a cheap lane on the highway for rollup trucks, allowing vast amounts of information to be posted without clogging the passing lane. The new Fusaka upgrade promises to expand this capacity further, raising the gas limit and introducing PeerDAS, a system where nodes sample data rather than storing it. It is a move toward a system where the network holds everything, but no single participant must hold more than a fraction.
RELATED: Bitcoin billionaire will serve time after British police broke down her door and arrested her in bed
 Photo by Vince Mignott/MB Media/Getty Images
Photo by Vince Mignott/MB Media/Getty Images
But the most radical application of this new approach lies in the “Verge,” a suite of upgrades intended to make the network “stateless.” The ambition is to allow a user with a basic laptop, or even a phone, to verify the chain. Through the use of Verkle trees — cryptographic accumulators that replace more cumbersome data structures — proofs of state become tiny, manageable things. Verification is broadened, flattening the hierarchy of nodes. In this future, we need not trust institutions or even the “full nodes” of the blockchain priesthood, but rather trust the math and verify the proof.
There is a detachment to this logic that appeals to the cypherpunk instinct. The implications are deeply social. In the classical world, trust was intimate; it required knowing a reputation, a face, a history. Ethereum replaces this personal trust with mathematical guarantees. It is a vision of accountability without surveillance. This affordance is particularly relevant in the realm of privacy, an area where the unblinking transparency of the blockchain has long been a liability.
The Privacy Stewards of Ethereum, a group operating within the Ethereum Foundation, have outlined a roadmap that seeks to make privacy a “first-class feature.” They speak of “private writes” and “private reads,” of enabling users to interact with the ledger without leaking their identity or intent. They reject the idea that scaling requires the sacrifice of privacy and posit that one might gain a degree of invisibility while the system enforces the rules so strictly that cheating becomes computationally impossible.
One could prove one is a unique human without revealing one’s name, or prove a vote was counted without revealing the ballot. It is a shift from universal transparency to a society of secret handshakes, where transparency is selective and discretionary.
Of course, the Ethereum roadmap has risks. There is the question of “gas limit politics,” the danger that the specialized hardware required to generate zero-knowledge proofs will reintroduce centralization by another name. There is the fragility of the new cryptography itself, the fear that a breakthrough in quantum computing could render these mathematical castles defenseless. There is the ever-present tension between the ideal of a decentralized network and the reality of complex governance.
Yet, the momentum is undeniable. The integration of a zkEVM at Layer 1, an implementation of the Ethereum Virtual Machine that generates proofs of the blocks themselves, represents the capstone of this overhaul. It is an attempt to scale to the level of global finance, to process hundreds of thousands of transactions per second, without utilizing trusted servers.
Ethereum aims to renovate digital society in real time, to reconcile the conflicting desires for scale, security, and privacy through a reliance on “moon math” that has suddenly, quietly become infrastructure. Ethereum is betting that cryptographic truth can substitute for consensus. It is moving toward a global notary that sees everything and nothing, verifying the unseen with absolute precision in a ballet of proofs, harmonizing to a music we are only just beginning to hear.
Star Wars: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Wants to Buy a Rocket Company to Take on Elon Musk’s SpaceX
AI may soon reach beyond Earth as OpenAI CEO Sam Altman looks to the stars for a solution to the growing energy demands of data centers. Altman is reportedly considering an investment in a rocket company to take on bitter rival Elon Musk’s SpaceX.
The post Star Wars: OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Wants to Buy a Rocket Company to Take on Elon Musk’s SpaceX appeared first on Breitbart.
CRASH: If OpenAI’s huge losses sink the company, is our economy next?

ChatGPT has dominated the AI space, bringing the first generative AI platform to market and earning the lion’s share of users that grows every month. However, despite its popularity and huge investments from partners like Microsoft, SoftBank, NVIDIA, and many more, its parent company, OpenAI, is bleeding money faster than it can make it, begging the question: What happens to the generative AI market when its pioneering leader bursts into flames?
A brief history of LLMs
OpenAI essentially kicked off the AI race as we know it. Launching three years ago on November 30, 2022, ChatGPT introduced the world to the power of large language models LLMs and generative AI, completely uncontested. There was nothing else like it.
OpenAI lost $11.5 billion in the last quarter and needs $207 billion to stay afloat.
At the time, Google’s DeepMind lab was still testing its Language Model for Dialogue Applications. You might even remember a story from early 2022 about Google engineer Blake Lemoine, who claimed that Google’s AI was so smart that it had a soul. He was later fired from Google for his comments, but the model he referenced was the same one that became Google Bard, which then became Gemini.
As for the other top names in the generative AI race, Meta launched Llama in February 2023, Anthropic introduced the world to Claude in March 2023, Elon Musk’s Grok hit the scene in November 2023, and there are many more beneath them.
Needless to say, OpenAI had a huge head start, becoming the market leader overnight and holding that position for months before the first competitor came along. On a competitive level, all major platforms have generally caught up to each other, but ChatGPT still leads with 800 million weekly active users, followed by Meta with one billion monthly active users, Gemini at 650 million monthly active users, Grok at 30.1 million monthly active users, and Claude with 30 million monthly active users.
Financial turmoil for OpenAI
Just because ChatGPT is the leading generative AI platform does not mean the company is in good shape. According to a November earnings report from Microsoft — a major early backer of OpenAI — the AI juggernaut lost $11.5 billion in the last quarter alone. To make matters even worse, a new report suggests that OpenAI has no path to profitability until at least 2030 or later, and it needs to raise $207 billion in the interim to stay afloat.
By all accounts, OpenAI is in serious financial trouble. It is bleeding money faster than it makes it, and unless something changes, the generative AI pioneer could be on the verge of a complete collapse. That is, unless one of these Hail Marys can save the company.
RELATED: GOD-TIER AI? Why there’s no easy exit from the human condition
 Photo By David Zorrakino/Europa Press via Getty Images
Photo By David Zorrakino/Europa Press via Getty Images
The bid to save OpenAI
OpenAI is currently looking into several potential revenue streams to turn its financial woes around. There’s no telling which ones will pan out quite yet, but these are the options we know so far:
For-profit restructure
When OpenAI first emerged, it was a nonprofit company with the goal to improve humanity through generative AI. Fast-forward to October 2025 — OpenAI is now a for-profit organization with a separate nonprofit group called the OpenAI Foundation. While the move will allow OpenAI’s profit arm to increase its earning potential and raise vital capital, it also received a fair share of criticism, especially from Elon Musk, who filed a lawsuit against OpenAI for reneging on its original promise.
A record-breaking IPO
Another big perk of its new for-profit restructure, OpenAI now has the power to go public on the stock market. According to an exclusive report published by Reuters in late October, OpenAI is putting the puzzle pieces together for a record-breaking IPO that could be worth up to $1 trillion. Not only would the move make OpenAI a publicly traded company with stock options, it would also give it more access to capital and acquisitions to further bolster its products, services, and economic stability.
Ad monetization
Online ads are the lifeblood of many online websites and services, from Google to social media apps like Facebook to mainstream media and more. While AI platforms have largely stayed away from injecting ads into their results, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman recently said that he’s “open to accepting a transaction fee” for certain queries.
In his ideal ad model, OpenAI could potentially take a cut of any products or services that users look for and buy through ChatGPT. This structure is different from how Google operates, by letting companies pay to bring their products to the top of search results, even if the products they sell are poorly made. Altman believes that his structure is better for users and would foster greater trust in ChatGPT.
Government projects and deals
While Altman recently denied that he’s seeking a government bailout for OpenAI’s financial troubles, the company can still benefit from government deals and projects, the most recent one being Stargate. As a new initiative backed by some of the biggest players in the AI space, Stargate will give OpenAI access to greater computing power, training resources, and owned infrastructure to lower expenses and increase the speed of innovation as they work on future AI models.
If OpenAI fails …
While OpenAI has several monetization options on the table — and perhaps even more that we don’t know about yet — none of them are a magic bullet that’s guaranteed to work. The company could still collapse, which brings us to our question at the top of the article: What happens to the generative AI market if OpenAI fails?
In a world where OpenAI fizzles entirely, there are several other platforms that will likely fill the void. Google is the top contender, thanks to the huge progress it made with Gemini 3, but Meta, xAI, Anthropic, Perplexity, and more will all want a piece.
That said, OpenAI isn’t the only AI platform struggling to make money. According to Harvard Business Review, the AI business model simply isn’t profitable, largely due to high maintenance costs, huge salaries for top AI talent, and a low-paying subscriber base. In order to keep the generative AI dream alive, companies will need a consistent flow of capital, a resource that’s more accessible for established companies with diverse product portfolios — like Google and Meta — while the new companies that only build LLMs (OpenAI and Claude) will continue to struggle.
At this stage in the AI race, there’s no doubt in my mind that the whole generative AI market is a big bubble waiting to burst. At the same time, AI products have been so fervently foisted on society that it all feels too big to fail. With huge initiatives like Stargate poised to beat China and other foreign nations to artificial general intelligence AGI, the AI race will continue, even if OpenAI no longer leads the charge. If I were a betting man, though, I would guess that someone important finds a way to keep Sam Altman’s brain child afloat one way or another, even as all signs point toward OpenAI spending itself out of business.
Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos are racing to enclose Earth in an orbital computer factory

In Memphis, Tennessee, where Elon Musk’s xAI initiative spun up a “compute factory” of some 32,000 GPUs, the local grid could not sustain the demand. The solution was characteristic of the era: 14 mobile gas turbine generators, parked in a row, burning fossil fuel to feed the machine. It was a scene of brute industrial force, a reminder that the “cloud,” for all its ethereal branding, is a heavy, hot, loud thing. It requires acres of land for the servers, rivers of water for cooling, and enough electricity to power a small nation.
The appetite of AI is proving insatiable. To reach the next plateau of synthetic cognition, we must triple our electrical output and are constrained by our capacity to do so. And so, with the inevitability of water seeking a lower level, the gaze of Silicon Valley has drifted upward. If the earth is too small, too regulated, and too fragile to house the machines of the future, we shall instead build them in the sky.
The high ground of the 21st century is not a hill, but an orbit.
The proposal is startling, in the way that leaps in engineering often are. In late 2025, Musk noted on social media that SpaceX would be “doing” data centers in space. Jeff Bezos, a man who has long viewed the planetary surface as a sort of zoning restriction to be overcome, predicted gigawatt-scale orbital clusters within two decades.
The pitch is seductive: In the vacuum of low-Earth orbit, the sun never sets. There are no clouds, no rain, no neighbors to complain. There are only the burning fusion of the sun and the cold of deep space, which turns out to be the perfect medium for cooling the heated circuits of a neural network.
The vacuum is valuable because it is an infinite heat sink. The sunlight is valuable because it is free voltage. The plan, as outlined by startups such as Starcloud (formerly Lumen Orbit), involves structures that defy terrestrial intuition. These are not the tin-can satellites of the Cold War but solar arrays and radiator panels four kilometers wide, vast shimmering sheets assembled by swarms of robots. These machines, using technology like the MIT-developed TESSERAE tiles, would click together in the silence, building a cathedral of computation that no human hand will touch.
RELATED: Trump leaves Elon Musk’s Grok, xAI off White House list of AI partners
 Photo by BRENDAN SMIALOWSKI/AFP via Getty Images
Photo by BRENDAN SMIALOWSKI/AFP via Getty Images
There is a stark beauty to the engineering. On Earth, a data center fights a losing battle against entropy, burning energy to pump heat away. In space, heat can be radiated into the dark. A server rack in orbit, shielded by layers of polymer and perhaps submerged in fluid to dampen the cosmic rays, swims in a bath of eternal starlight, crunching the data beamed up from below. Companies such as NTT and Sky Perfect JSAT envision optical lasers linking these satellites into a single, glowing lattice: a cosmic village of information.
Yet one cannot help but observe its fragility. The modern GPU is a miracle of nanometer-scale lithography, a device so sensitive that a stray alpha particle can induce a chaotic error. The environment of space is hostile, awash in the very radiation that these chips abhor. To place the most delicate artifacts of human civilization into the harshest environment known to physics is a gamble. The engineers speak of “annealing” solar cells and triple-redundant logic. The skeptic notes that a bit-flip in a language model is a nuisance, while a bit-flip in a battle management system is a tragedy.
There is also the matter of the debris. We have already cluttered orbits with the husks of our previous ambitions: spent rocket stages, dead weather satellites, flecks of paint moving at 17,000 miles per hour. To introduce massive, kilometer-scale structures is to invite the Kessler syndrome, a cascade of collisions that could imprison us on the surface for generations. We are proposing to solve the environmental crisis of terrestrial computing by potentially creating an environmental crisis in the exosphere. It is the American way, the frontier way: When one room gets messy, simply move to the next, larger room.
The drive to do this is not merely economic, though the economics are potent. If Starship can lower the cost of launch to under $200 per kilogram, the math begins to close. If energy in space is effectively free, the initial capital outlay is justified by the lack of a monthly utility bill. But the impulse is also older, that of the Russian scientist and mathematician Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, who called Earth the “cradle” of humanity, which, like a mature human being, eventually we must leave. We are seeing the embryonic stages of the “noosphere,” a sphere of pure mind encircling the planet. By exporting our cognition to the heavens, we are externalizing our logic. The logos of our civilization will physically reside above us, a silent pantheon of servers ordering and facilitating the lives of the creatures below.
There is a geopolitical texture to this as well. The concept of “sovereign cloud” takes on a new meaning when the data center is orbiting over international waters. Intelligence agencies and defense contractors are quietly investing, sensing that the high ground of the 21st century is not a hill, but an orbit. To control the compute is to control the speed of thought.
Whether this will work remains to be seen. The history of spaceflight is a graveyard of optimistic PowerPoints. It is possible that the radiation will act as a slow acid on the silicon, that the robotic assembly will jam, that the cost will remain stubbornly high. But the momentum is real. The mobile gas turbines in Memphis are a stopgap. The data centers consuming the aquifers of Arizona are a liability. The logic of the market and the machine points upward.
We stand at a peculiar intersection. We are attempting to use the most primal forces of the solar system, the burning star and the freezing void, to power our most refined tools. It is a grand, ambitious, and entirely human endeavor. We are building a computer in a jar and hanging the jar in the sky, hoping that the view will be clear enough to see the future.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang Praises Trump on Joe Rogan Podcast: ‘Very Practical, Common Sense, and Logical’
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang praised President Donald Trump on Wednesday, telling podcaster Joe Rogan that “everything” the president “thinks through is very practical, common sense, and logical.” Jensen also credited Trump’s energy policy with saving AI, telling Rogan, “Without energy growth, we can have no industrial growth. And that was what saved the AI industry.”
The post Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang Praises Trump on Joe Rogan Podcast: ‘Very Practical, Common Sense, and Logical’ appeared first on Breitbart.
Rejoice, Jared Leto fans! Time to fall asleep on your couch watching ‘Tron: Ares’

This week, “Tron: Ares,” the blockbuster that wasn’t, makes its final bid for profitability — hitting the streaming services, complete with a bonus deleted scene. As Hollywood continues its messy quest to restore its lost glory, what better time for a postmortem?
“Tron: Ares” tells us much. This trilogy-completing movie should have been a layup. With the film, Disney had a great existing piece of intellectual property and a time that could not have been better for a sequel. You can’t go a day on the internet without hearing about AI, surveillance, data centers, hacking, and other topics that the “Tron” universe is uniquely qualified to address.
I need to defend Jared Leto for a second.
The question was: Could Disney pull off a sequel to a pair of movies released in 1982 and 2010 while delivering a quality film that made compelling points on the future of Big Tech and the ever-changing interplay between AI and humanity? The Disney modus operandi is usually to serve up a disappointing experience of woke talking points, lazy writing, and uninspired filmmaking. “Tron: Ares” offered the studio the chance to buck that trend.
The centerpiece of the “Tron” universe is a digital world called the Grid. For the uninitiated, this alternate world, existing inside computer systems, appears as a neon-lit, mirror-smooth alternative to our own. Computer programs inhabit humanoid forms and live in strict, hierarchical societies.
Its well-crafted lore merits a catch-up. In the original “Tron” movie (1982), brilliant programmer Kevin Flynn is attempting to hack into the system of his former employer, ENCOM, to prove that another employee, Ed Dillinger, plagiarized Flynn’s work to get ahead at the company. Flynn ends up getting transported onto the Grid via particle laser and battles the Master Control Program that is attempting to influence the real world. He is successful, proves that Dillinger plagiarized his work, and ends up as CEO of ENCOM. The franchise gets its title from a program named Tron, which fights alongside Flynn.
In “Tron: Legacy” (2010), Kevin Flynn expands his Grid and ends up getting stuck there, vanishing from the real world. His son Sam has inherited control of ENCOM, now a top tech company, but refuses to step into a leadership role. He goes looking for his father and ends up having his own adventure on the Grid, working alongside his father to outwit Clu, the program that betrayed his father and took control of the Grid. His father sacrifices himself to allow Sam to escape back to the real world along with Quorra, a female “isomorphic algorithm.” That is, a computer program manifested onto the Grid without any human contribution. Sam and Quorra end the film setting out to make the world a better place with the grid technology.
High concept, low plot
Here’s where the slapdash takes over from the archetypal. “Tron: Ares” picks up 15 years later with a healthy dose of the now-classic Disney bait and switch. Forget Sam, Quorra, Tron, or any of the popular characters from the previous installments. Sam, in a “somehow, Palpatine returned”-level move, has “left ENCOM for personal reasons.” Instead, we are introduced to his replacement: Eve Kim (Greta Lee). The bait and switch, along with other now-classic Disney tropes, is present throughout the film, but more on that later.
Let’s break down the plot. (Warning: inevitable spoilers below.)
RELATED: Bad performance or bad politics? A list of the most hated actors
 Photo by Jean Catuffe/GC Images
Photo by Jean Catuffe/GC Images
There are two massive tech companies: ENCOM Technologies, now run by Eve Kim, and Dillinger Systems, run by Julian Dillinger, the grandson of Ed Dillinger from the first movie. These companies have figured out how to use particle lasers to bring things from the Grid into the real world. They basically just 3D-print tanks, ships, trees, people, anything at all, using nothing but electricity. How does that actually work? Never mentioned.
These Grid creations only last 29 minutes before disintegrating into dust and reappearing on the Grid. Eve Kim is determined to solve this problem by finding the permanence code, which Kevin Flynn supposedly hid somewhere. She holes up in Flynn’s old hideout in Alaska and starts looking for it while her male assistant, Seth Flores (Arturo Castro), sits around eating breakfast burritos and complaining that she doesn’t pay enough attention to him. Meanwhile, Dillinger Systems is presenting its new Master Control Program, Ares (Jared Leto). Julian Dillinger leaves out the fact that Ares only lasts 29 minutes, for which he is reprimanded by his mother (Gillian Anderson), who provides the conscience and competence at Dillinger.
Eve finds the permanence code and successfully tests it, then gets a call from ENCOM’s necessarily diverse CTO Ajay Singh (Hasan Minhaj). He tells Eve that Dillinger has hacked ENCOM’s server and caused all sorts of damage. Basically, Julian learned that Eve has the permanence code, and he wants to get his toxic white hands on it.
The rest of the movie is a series of action scenes strung together by the bare bones of a story. Ares is sent into the real world to get the code from Eve. He comes close, forcing her to destroy the flash drive, but fails when he hits his 29-minute shot clock. Eve is then transported onto the Grid when another Dillinger agent shoots her with a particle gun. Once there, the code can be extracted from her now-digital mind. This process would kill her, but Julian orders Ares to proceed. Ares, who has shown signs of straying from his programming, goes rogue and helps her to escape, asking for the permanence code in return so that he can live in the real world. Eve agrees, and the rest of the movie is basically them running around trying to get the code (remember, Eve destroyed the drive, so now they have to find it again) before Dillinger’s new MCP, Athena (Jodie Turner-Smith), catches them.
They end up finding a way to access it on Kevin Flynn’s old computer and send Ares onto the original Grid from the first “Tron” movie. Once there, he meets Kevin Flynn, or rather some sort of aspect or memory of him — it is never made clear — and gets the permanence code after Flynn determines that he is suitably curious (or something) enough to become human. Meanwhile, Athena is determined to catch Eve and brings a few Grid vehicles into the real world for a rather underwhelming final battle.
Things wrap up when Ares arrives back in the real world just in time to save Eve, while Ajay and Seth hack the Dillinger mainframe and shut it down, disabling Athena, whose sympathetic death scene feels like a DEI box-check. The film concludes with Eve using the permanence code to lead ENCOM in transforming various industries and Ares wandering the world under cover, learning how to live among humans.
The good, the bad, and the utterly predictable
There are three main takeaways from this film, but first I need to defend Jared Leto for a second. I know there are plenty of reasons, professional and otherwise, for people to dislike Leto, and I’m not necessarily disagreeing with them. However, I thought his performance in this film was quite good. The physical choices he makes in portraying his AI character add a subtle, uncanny-valley aspect to Ares. The best part of the performance, though, is the vocal work. Leto manages to give a digital quality to Ares’ speech without resorting to crude robotic tones. He uses careful pitch and tone changes and curates his pauses to give the effect of an LLM responding to a prompt, without losing the organic quality of human voice and speech. It is very well done, and the delivery works perfectly with the dialogue written for his character.
I’ve seen a lot of complaints about the acting in “Tron: Ares,” and some of it is warranted. However, as is so often the case, people are blaming the actors when a large part of the problem is bad dialogue. Seriously, you try turning the line “I don’t like sand; it’s coarse and rough and irritating, and it gets everywhere. Not like here. Here everything is soft and smooth” into an earnest, romantic phrase. The acting in “Tron: Ares” is mostly fine, and in Leto’s case, it is very impressive. Sure, it’s not all amazing, but the dialogue is clearly the bigger issue. The exception is the portion written for Ares. I suppose feeding prompts into ChatGPT actually worked in that case.
Another issue is the Disney tropes that permeate the film. They didn’t bother me that much because they are so worn out at this point. There is, of course, the IP bait and switch, in which a studio baits an audience with a familiar IP, character, etc. and then switches it out for a DEI replacement. Throwing out the entire Flynn family and replacing them with a diverse CEO girlboss is the relevant example here. If you’re still falling for this move in A.D. 2025, let me just say, as a longtime “Star Wars” fan, you wouldn’t last an hour in the asylum where they raised me.
Like any modern Disney movie, “Ares” adheres to what we might call the CCCC: color and chromosome competence correlation. Eve is a woman of color and therefore exceedingly competent and driven. Her Hispanic assistant, Seth, is light enough to be belittled for his manhood, but diverse enough to be portrayed as a competent force for good. Ajay, the CTO, is an Indian man. His complexion is darker than Seth’s, making him more competent. The film makes certain we know it is Ajay who actually manages to get into the Dillinger mainframe. However, being Indian means he is not dark enough to be excluded from male penalties. Therefore, he gets a personality that is Kash Patel turned tech bro, and part of his competence and drive are outsourced to his female assistant, Erin.
The CCCC applies across the moral spectrum. Julian Dillinger might be an evil tech villain, but he is also a white man and cannot, therefore, be competent or have real authority. These qualities are supplied by his mother, Elisabeth. Athena, the program who takes over as the Dillinger MCP, is played by a black woman (get it — Black Athena?) and is therefore competent and driven. Her failure is not her fault, but the result of Ajay truth-nuking the Dillinger Grid. In “Ares,” these tropes were too worn out to be troubling; they were just boring. I’m tired of being able to predict films after a passing glance at the principal characters.
Like the tropes, the film’s treatment of AI is just boring. The “Tron” universe is full of interesting AI potential, but “Ares” doesn’t go for any of them. The permanence code, which is a double helix as opposed to regular binary code (maybe I’m just a tech neophyte, but I thought that was cool), is never explained or explored. There is no real attempt to look at what the 3D-printed Grid creations actually are and what makes them work. If you can digitize a person’s mind by bringing him onto the Grid, that opens up all kinds of fascinating possibilities. “Ares” does not explore any of these paths. Rather, it goes for the same old “what if AI started becoming human” line that is pretty worn out at this point. Gareth Edwards’ “The Creator” did the whole “you should empathize with AI when it acts human” routine much better, but it isn’t very convincing in that film, either. In “Tron: Ares,” the wasted potential just makes the result more frustrating, which brings us to the final point and the biggest issue I have with the film.
At the end of the day, “Tron: Ares” is slop. It is content conceived and designed to be just that and nothing more. AI could have written this film, which might be by design (in which case, my apologies, Jesse Wigutow, I was not familiar with your game), but I don’t think so. It is not just the lack of explanations or the fact that anyone with an IQ above room temperature could predict the entire film after 10 minutes. Everything in this film feels like it was cut and pasted from a general template for “popular high-budget sci-fi movie.”
Who will take these missed opportunities?
So what went wrong? Well, leaving aside the obvious “don’t be woke” talking point, the main issue was misunderstanding the sort of IP the filmmakers were dealing with. At its core, “Tron” is a story about computers, not just a sci-fi universe of shiny alternate realities. Ignoring this fact robs “Ares” of the necessary thematic continuity for any good sequel. Instead, the film relies on cheap nostalgia and throwaway references, refusing to use the unique set of tools it has to tell a compelling story.
To take just one example, the ability to digitize the human mind — that alone offers a more compelling and relevant story. If you can digitize the human person, storing people on the grid, what does that say about the human soul? What does it mean for surveillance, incarceration, and memory? In a time of privacy concerns and AI data-farm controversies, a computer server with the ability to store, alter, or destroy human consciousness — not to mention the capacity for independent evolution and generation — sets up a whole list of compelling questions, themes, and plot points.
If you want to understand what I’m getting at, compare the soundtrack — an album by Nine Inch Nails that sounds more like GPT — to the “Tron: Legacy” soundtrack by Daft Punk, a now-legendary, pitch-perfect expression of the computer/reality synthesis that the franchise just couldn’t live up to.
The soundtrack isn’t the only place where “Tron: Ares” is a downgrade from “Legacy.” So let me offer some advice: If you find yourself looking to stream an AI-themed sci-fi movie, just watch “Tron: Legacy.” It’s not perfect, but the soundtrack is great, the CGI holds up well, and the writing and acting actually bear the mark of real human beings.
Strap ’em on: From watches to glasses, snag our top wearables this Black Friday
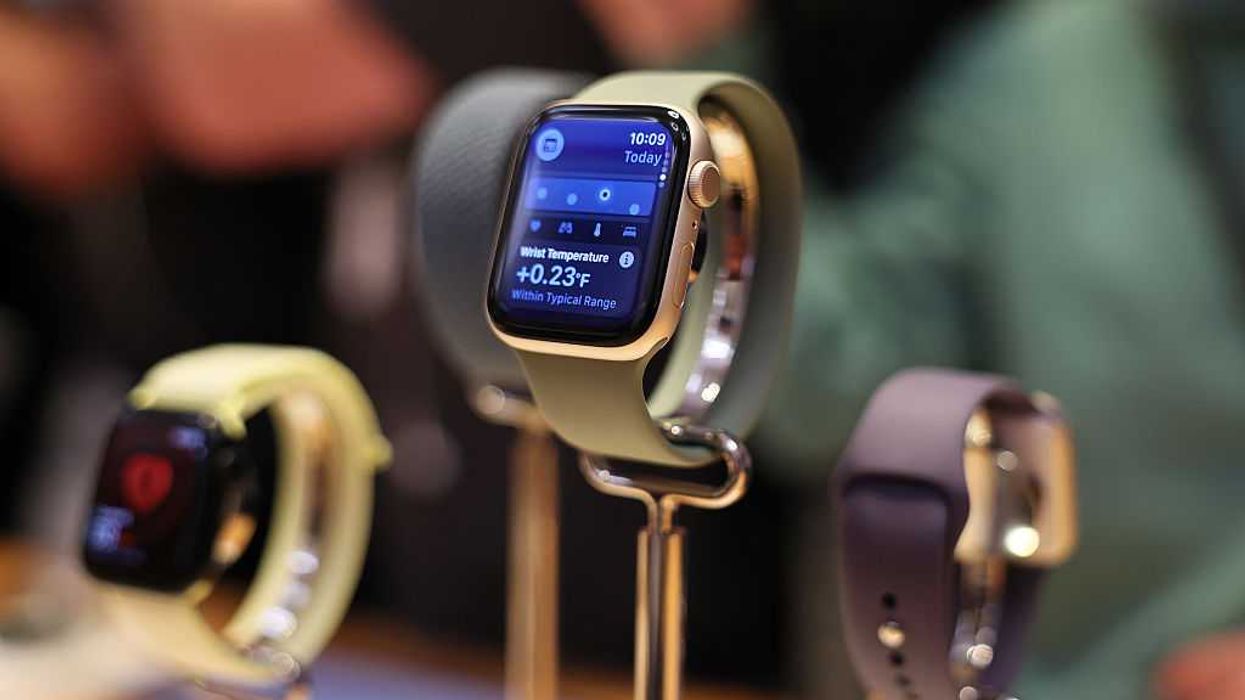

The speed of tech is a formidable force, so we have paused to catch you up on the cutting-edge devices and gadgets you might want to bump to the top of your list if you’re hoping to speedrun Black Friday this year.
Best wearables to buy during Black Friday
Apple Watch Series 10 or 11
Apple Watch is one of the best-selling wearables on the planet, largely due to its customization options, iconic style, and wide range of fitness features. However, while Apple used to add fun new sensors and capabilities every year, newer Apple Watches have reached a point of innovation stagnation. Aside from battery life improvements, last year’s Series 10 has all the new features that landed on the Series 11, including high blood pressure detection and sleep score tracking, plus all the usual tricks like heart rate monitoring, ECG scans, blood oxygen levels, AFIB detection, and more.
There’s no telling how long the gadgets on your list will be on sale.
While I do recommend an Apple Watch for anyone in the Apple ecosystem, your money would be better spent on a Series 10, if you can find one. Otherwise, you’re looking at $399 MSRP or more for a Series 11.
 The Series 11 looks great, but for your money, the Series 10 wins out.Photo courtesy of Apple
The Series 11 looks great, but for your money, the Series 10 wins out.Photo courtesy of Apple
Pixel Watch 3 or 4
On the Android side, Pixel Watch has quickly become one of the best wearables available. With Fitbit integration, heart rate tracking, daily readiness scores, and a host of other features, Pixel Watch is the best that Android users can buy. As for which model deserves a spot on your wrist (or list), last year’s Pixel Watch 3 is where the device really started to hit its stride, while the newest Pixel Watch 4 for $349.99 adds quality-of-life improvements (40 hours of battery life per charge and a larger domed display) that further refine the experience. You’d be safe with either one of these under the tree this season.
![]() The Pixel Watch 4: just like the 3, only better.Photo courtesy of Android
The Pixel Watch 4: just like the 3, only better.Photo courtesy of Android
Oura Ring 4
For anyone who wants an ultra-sleek or unconventional wearable fitness tracker, Oura Ring 4 is easily the best ring the company has ever made. With a new slimmer design, it looks more like a piece of jewelry than a tech gadget. It comes in a range of sizes and finishes from $249 to $499, and it tracks everything you’d expect from a larger smartwatch, including heart rate data, sleep and rest, and stress levels. Although Oura Ring is great for men and women, its added female health features make it especially great for the lady in your life.
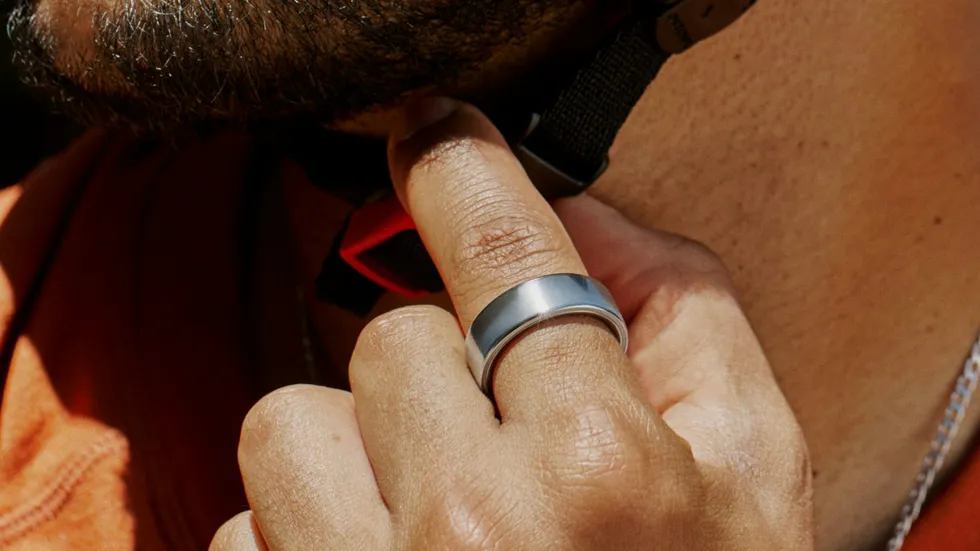 Oura Ring 4 hits new highs.Photo courtesy of Oura
Oura Ring 4 hits new highs.Photo courtesy of Oura
One more thing: Speaking of Fitbit, it’s easy to recommend a Charge series fitness band or Versa watch to anyone looking to slim down in the New Year. However, hold off for now. Google recently confirmed that new devices are on the way soon, so only buy a Fitbit this week if you get a really good discount.
Try something totally new for Black Friday
For the more adventurous gift-giving type, a new product category is making waves in the tech space. From Apple to Google, Meta and more, everyone is trying their best to make augmented reality, virtual reality, and extended reality glasses, goggles, and headsets a thing. The category is still very young and OEMs are still trying to figure out exactly what users want, but if you’d like to try it out for yourself or with a loved one, here are a few devices to keep in mind.
Apple Vision Pro
Apple’s first foray into AR didn’t go so well. The first-generation Vision Pro was heavy, clunky, and very expensive. It didn’t sell in high numbers, either. However, that didn’t stop Apple from finally launching a sequel that hit shelves last month. With a much faster M5 chip and an improved dual-knit headband for comfort, the second-generation Vision Pro offers an immersive spatial computing experience that puts you directly inside your work, movies, and memories. If you ever wanted to know what it was like to wear an iPad on your face, this is the one to do it.
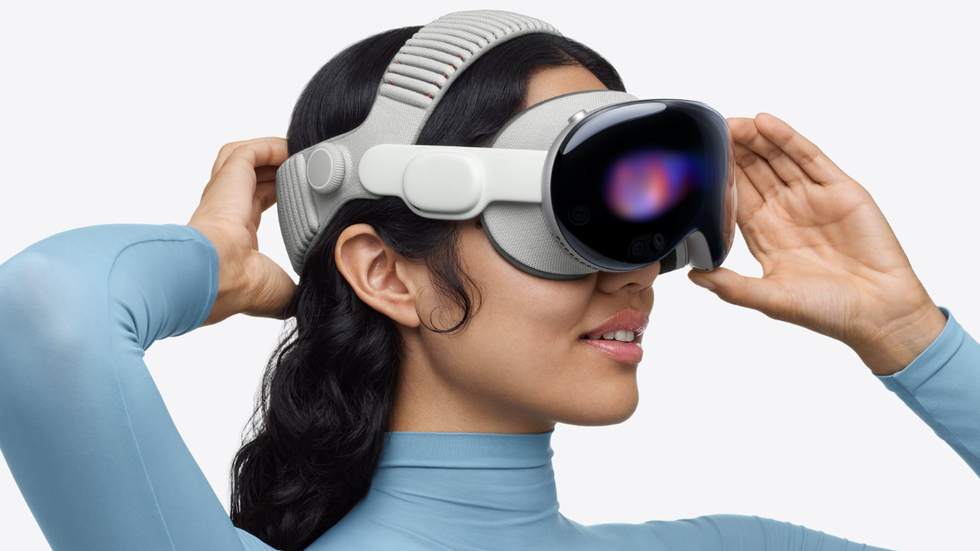 First was worst, second is best: the new Vision Pro.Photo courtesy of Apple
First was worst, second is best: the new Vision Pro.Photo courtesy of Apple
One more thing: Vision Pro is an impressive piece of tech, but keep in mind that developers have been slow to create apps for the headset. Nearly two years after the first version launched, several critical apps are still missing from the App Store, including YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify. At this point, there’s no telling if or when the platform will ever take off like iPhone, Apple Watch, and Mac, so only pick this one up if you’re really curious about AR/VR/XR.
RELATED: Fooled by fake videos? Unsure what to trust? Here’s how to tell what’s real.
 Qilai Shen/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Qilai Shen/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Samsung Galaxy XR
Almost one full year ago, Google announced its glasses operating system called Android XR. Even then, the company hinted that the first Android XR device would come from Samsung, and after months of teases and unveils, it is finally here. Samsung Galaxy XR is Android’s first direct Apple Vision Pro competitor. Using the same concept — building a product that lets users dive directly into the action — Galaxy XR differentiates itself in several key ways. For starters, Gemini sits at the center of the user experience, helping users navigate the UI, pull up information, and learn more about whatever they see on their screens. The device itself is also lighter than Vision Pro, making it easier to wear for longer sessions. Android XR supports most apps already found on the Google Play Store, which means it does have access to YouTube, Netflix, and other entertainment apps, all ready to go.
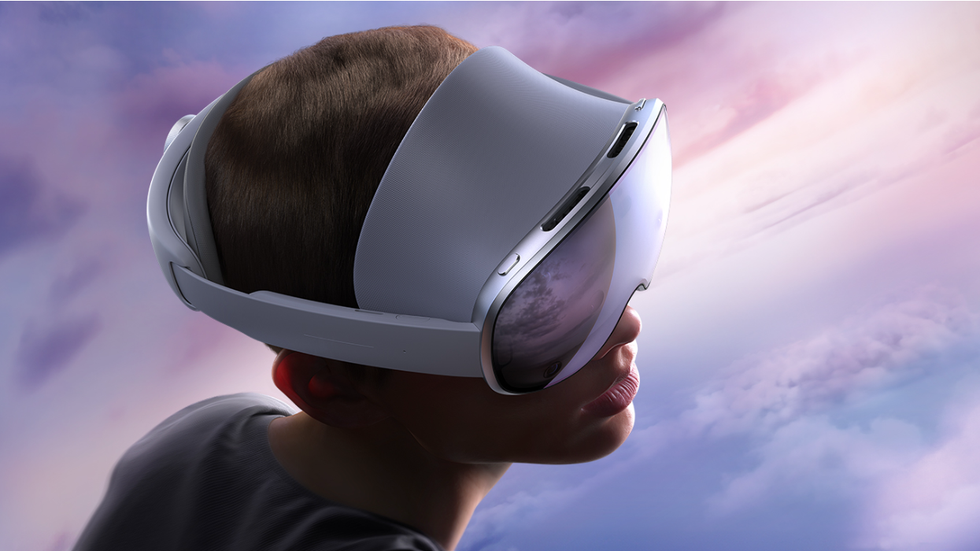 Samsung’s Galaxy XR wants you scrolling past the Vision Pro.Photo courtesy of Samsung
Samsung’s Galaxy XR wants you scrolling past the Vision Pro.Photo courtesy of Samsung
One more thing: While Samsung Galaxy XR is an interesting alternative to Apple Vision Pro, its underlying software is brand-new. Developers will likely make tweaks and squash bugs as they flesh out the feature list for Android XR. It’s also worth noting that Google has a reputation for killing projects early if they don’t amass a large user base within the first several years. In other words, if the Samsung Galaxy XR isn’t a success, Android XR may get the axe sooner than later. No one has a crystal ball, though, so it’s hard to predict what will happen until a bit more time has passed.
Ray-Ban Meta Glasses (Gen 2)
Where Apple Vision and Samsung Galaxy XR are meant to be worn while sitting down in a controlled space, Ray-Ban Meta Glasses (Gen 2) are smart glasses that are meant to be worn with you out in the world. These don’t have displays, but they have built-in cameras controlled by an AI assistant that can see what you see and tell you about the world around you in real time. Ask it about the architecture of a building, capture high-quality videos and photos of memories as they happen in front of you, or play music through the built-in open-air speakers. If you ever wanted an AI assistant for your face, Ray-Ban Meta Glasses (Gen 2) are a good place to start.
 Play it cool with the new Meta Glasses, and you might not get the wrong kind of stares.Photo courtesy of Ray-Ban/Meta
Play it cool with the new Meta Glasses, and you might not get the wrong kind of stares.Photo courtesy of Ray-Ban/Meta
Let the deals begin!
The Black Friday deals have already started to roll out, and many of them will carry into Cyber Monday and the weeks leading up to Christmas. Still, there’s no telling how long the gadgets on your list will be on sale, so grab them sooner rather than later to make sure you have exactly what you want under the tree.
Happy Black Friday weekend and merry Christmas!
search
categories
Archives
navigation
Recent posts
- Liza Soberano, Ogie Diaz reconnect after 3 years January 11, 2026
- Dasuri Choi opens up on being a former K-pop trainee: ‘Parang they treat me as a product’ January 11, 2026
- Dennis Trillo addresses rumors surrounding wife Jennylyn Mercado, parents January 11, 2026
- Kristen Stewart open to ‘Twilight’ franchise return, but as director January 11, 2026
- NBA: Five Cavs score 20-plus points as Wolves’ win streak ends January 11, 2026
- NBA: Hornets sink 24 treys in 55-point rout of Jazz January 11, 2026
- NBA: Victor Wembanyama, De”Aaron Fox score 21 each as Spurs top Celtics January 11, 2026






