
Category: Opinion & analysis
Abortion • Blaze Media • Dobbs v. jackson women's health organization • March for Life • Opinion & analysis • Roe v. wade
Nash Keen’s life proves the unborn deserve the law’s protection
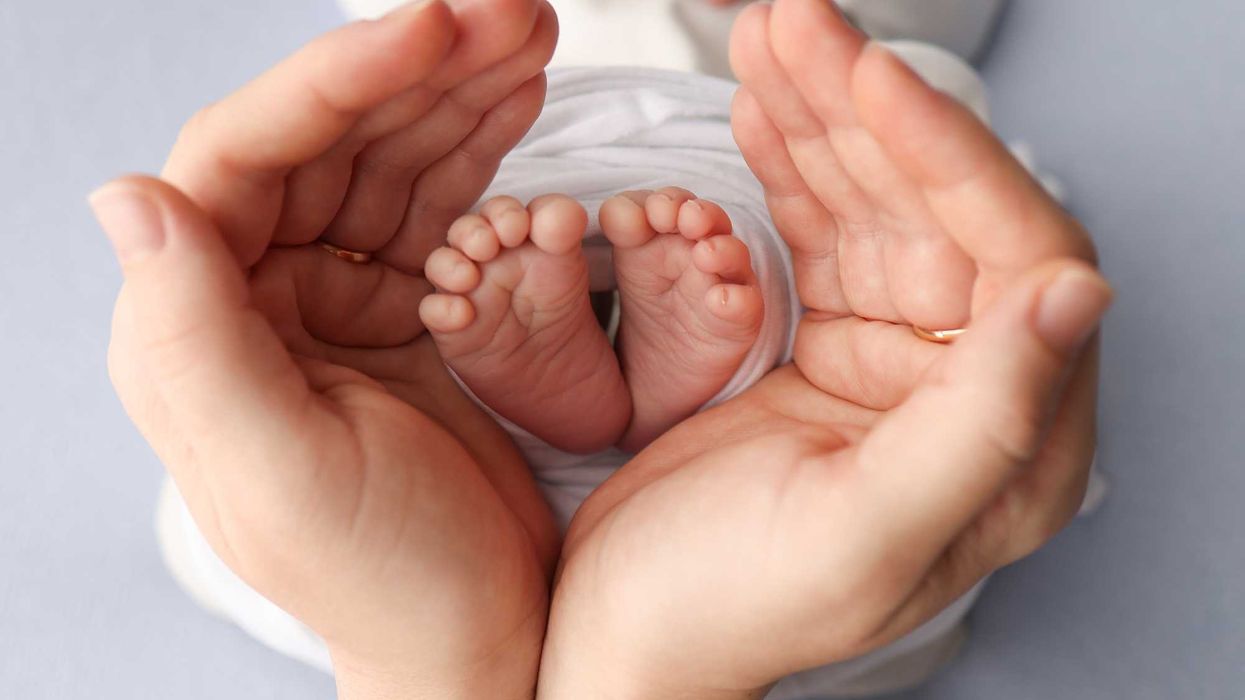

Nash Keen holds the Guinness World Record for the most premature infant to survive outside the womb. Born at just 21 weeks’ gestation, Nash’s story forces us to grapple with an unsettling reality: In 29 states and Washington, D.C., the law would have permitted his abortion for at least another week.
At 21 weeks, abortionists commonly use dilation and extraction. Many call it a dismemberment abortion, and the term fits. The procedure requires pulling the child apart.
We’ve made real progress since the Dobbs decision. Thirteen states, including my home state of West Virginia, protect life from the moment of conception.
A Sopher clamp — a metal tool with sharp, serrated jaws — grasps a limb, the torso, or the head. The abortionist twists and tears the body piece by piece. The child has a beating heart and can feel pain. Arms and legs are ripped from the torso. The spine snaps. The skull is crushed so it can pass through the cervix. Blood and tissue are suctioned out. Then the abortionist reassembles the remains on a tray to confirm nothing is left behind.
This barbarity happens tens of thousands of times each year in the United States.
Consider the contrast. At 21 weeks, doctors and nurses fought to keep Nash alive. At the same stage of development, in other hospitals and clinics across the country, medical professionals ended the lives of other babies.
What separates those children? No coherent answer exists because no meaningful difference exists. Every child — born and unborn — bears God-given dignity and deserves the protection of our laws.
This year, Nash will turn 2. His survival, as rare as it is, reveals why so many Americans fight for life — and why we will win.
I plan to do everything I can to protect the most vulnerable among us. That’s why I’m proud to co-sponsor the Life at Conception Act, which aligns federal policy with scientific reality: Life begins at conception, and the law should protect it.
Policymakers must also do more to support mothers and fathers raising children. If we aim — as we should — to end abortion, our laws must protect the unborn and make it easier to raise a family in America.
RELATED: New York caves on forcing nuns and churches to fund abortion after knockout SCOTUS ruling
 Photo by JOSEPH PREZIOSO/AFP via Getty Images
Photo by JOSEPH PREZIOSO/AFP via Getty Images
That’s why I have introduced legislation to give low-income families more flexibility to choose the child-care option that fits their situation.
I have also introduced legislation to eliminate marriage penalties that discourage single parents from marrying.
And I have also introduced a bill to close a loophole so women who choose not to return to work after giving birth cannot be forced to reimburse an employer for health insurance premiums from the year they delivered.
Similarly I support legislation that would hold fathers accountable for pregnancy costs as part of child support. I supported expanding the Child Tax Credit in the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, and I advocate extending the credit to cover the months of pregnancy.
We’ve made real progress since the Dobbs decision. Thirteen states, including my home state of West Virginia, protect life from the moment of conception. In Congress, the One Big Beautiful Bill Act finally defunds big-abortion providers.
The fight has only begun. As long as I’m in public service, I will work to protect every life from the moment of conception — and to ensure federal policy puts the American family first.
The GOP can’t ‘wield’ the administrative state without being corrupted by it

Many Americans have watched Peter Jackson’s movie trilogy “The Lord of the Rings.” And many have read J.R.R. Tolkien’s books. Some can quote whole passages and trace Tolkien’s deliberate references to the life of Christ and the horror of modern war.
Maybe House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-La.) and Senate Majority Leader John Thune (R-S.D.) live in that camp. If not, they should.
The Republicans’ plan cannot be ‘use federal power while we have it, then trust the next guys.’
A crucial scene comes early in the saga. The council debates what to do with the One Ring, the ultimate source of power. Boromir makes an understandable, dangerous suggestion — a perfect expression of fallen man’s temptation: “Give Gondor the weapon of the enemy. Let us use it against him.”
Aragorn stops him with two sentences rooted in humility and truth: “You cannot wield it. None of us can.”
That is the lesson Republicans must learn now, while they still hold majorities.
Dismantle the machine, don’t borrow it
Many supporters of President Trump want Congress to act boldly. They also want something more important: They want Republicans to roll back the reach and scope of the federal government while they can. If the GOP refuses, Democrats will inherit the same machinery and use it without restraint. Not someday. Soon.
If you think I exaggerate by calling Democrats the enemy or warning that we are doomed, consider a recent message from the second-highest-ranking elected congressional Democrat in the country, House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries of New York. Jeffries posted a video of White House adviser Stephen Miller on X.com and wrote: “Donald Trump will leave office long before the five-year statute of limitations expires. You are hereby put on notice.”
Jeffries did not allege a crime. He did not explain what Miller did wrong. He did not argue facts or law. He issued a threat: We will punish you later because we can.
That is what Republicans keep forgetting. The federal government’s power does not idle in neutral. It exists to be used. If it remains in place, someone will use it — and progressives have already shown what they want to do with it.
Which raises the central point: Nobody can safely wield that power. Not congressional Republicans. Not any administration. The correct move is not to grab the weapon and promise better behavior. The correct move is to destroy the weapon.
Fraud stories shine a bright light
Start with something as basic as fraud.
Look at the unraveling of the Somali day-care scandal in Minnesota and the billions of stolen tax dollars. That story grew so large that it helped end Minnesota Democrat Gov. Tim Walz’s re-election ambitions. Yet the government did not uncover it.
Not the Government Accountability Office. Not the Congressional Budget Office. Not the Office of Management and Budget. Not House or Senate oversight committees. Not the IRS. Not the Small Business Administration. Not the armies of full-time staffers inside federal agencies reporting up to inspectors general whose job description exists for this very purpose.
All that government power — and it did nothing.
RELATED: America now looks like a marriage headed for divorce — with no exit
 mathisworks via iStock/Getty Images
mathisworks via iStock/Getty Images
The scandal came to light because of the tenacity of a 23-year-old guy with a camera. If the federal machine can miss fraud on that scale, imagine what else it misses.
Fraud saturates the system. Estimates run as high as $500 billion — roughly 7% of the $6.8 trillion federal budget. That budget still reflects COVID-era spending levels. In 2019, Washington spent $4.45 trillion. Why did we never return to pre-COVID levels?
Because money is power. And like Boromir, too many people convince themselves they can wield it.
Ethics are not enough
Energy policy shows the same temptation in real time.
My nonprofit organization, Power the Future, sent another letter to House and Senate oversight committees and to Attorney General Pam Bondi urging investigations into Biden’s energy secretary, Jennifer Granholm. In the final days of the Biden administration, Granholm awarded $100 billion in green-energy grants — more than the previous 15 years combined. Many recipients had previously supported her political campaigns.
Green money poured out of Washington through the misnamed Inflation Reduction Act, which allocated $60 billion for “environmental justice” — a phrase so deliberately amorphous that it has no fixed meaning. Team Biden spent $1 trillion “going green,” a statistic Vice President Kamala Harris bragged about during her lone 2024 debate with Donald Trump.
That entire structure still stands.
Nothing prevents the current energy secretary, Chris Wright, from spending billions on his favorite projects except his ethics. I believe Wright has ethics in abundance. We should feel grateful. But one man’s ethics do not qualify as a system of government.
The next secretary could be worse than Granholm. If the power remains, someone will use it.
RELATED: Nuke the filibuster or brace for the next impeachment campaign
 Viktoriia Melnyk via iStock/Getty Images
Viktoriia Melnyk via iStock/Getty Images
Empty the arsenal
Just as in Tolkien’s masterpiece, our enemies do not wait quietly. They scheme. They train. They amass armies of lawyers, activists, operatives, and bureaucrats. They build institutional pipelines that outlast elections. They do not go home after losing once. They plan the return.
Republicans need to plan as well — and their plan cannot be “use federal power while we have it, then trust the next guys.”
One party will not hold Washington forever. When conservatives lose power, they should make sure the left inherits a reduced federal government: weaker, narrower, stripped of the patronage systems and enforcement tools that now function as political weapons.
That is why it is incumbent upon congressional Republicans to do everything in their power — everything — to destroy the Ring.
America’s founders envisioned a weak federal government for this reason. In America’s 250th year, Congress should act like it understands the danger of concentrated power. If Republicans keep the machinery intact, they will regret it. If the Ring finds its next master, it will not spare the people who once held it.
Google’s new motto: Don’t be Christian

Google once had an informal motto: “Don’t be evil.” How about be ideologically driven? Opaque? Arbitrary?
Google sells itself as online Switzerland — a neutral search engine that doesn’t tilt one way or the other. That neutrality vanishes fast when you search for something its algorithm doesn’t like. Suddenly the thing you want becomes strangely hard to find unless you already know exactly where it lives. If you don’t, good luck.
You can’t fix what you’re not allowed to understand.
And good luck advertising it, too — if Google disapproves.
Most people still think of Google as a search engine. That’s outdated. Google is the 900-pound gorilla of online advertising through Google Ads. It has vacuumed up so much of the market that anyone who wants to advertise online usually has to go through Google’s pipeline, under Google’s terms, with Google acting as judge and jury.
This isn’t the print era, when advertisers bought space from newspapers and magazines directly, publication by publication. Today, a huge share of the ad economy runs through a single gatekeeper.
Some might call that a monopoly. Monopolies become even more dangerous when they turn ideological.
Google — and it is far from alone — leans hard left. It dislikes conservative and Christian content, and it has learned how to suppress it without leaving fingerprints. It buries the content in search rankings so that almost no one sees it unless they already know where to look. It throttles monetization. It blocks ads with vague warnings and “policy” language designed to end the conversation.
Google and TikTok now appear to be doing the same thing to faith-based content.
Have you heard of TruPlay? Probably not. That’s the point.
TruPlay is an entertainment app that offers faith-based games and videos for kids. It’s explicitly family-friendly — no sexual themes, no violence, no garbage disguised as “content.” Parents want that. Millions of them. There’s a market for wholesome screen time, and there’s money to be made providing it.
But according to the American Center for Law and Justice, Google has refused to do business with TruPlay for ideological reasons. The ACLJ says Google rejected TruPlay’s efforts to launch advertising campaigns, citing “religious belief in personalized advertising.”
Read that again. Google flagged religious belief as the problem.
The ACLJ says TruPlay tried to comply, filing appeals and revising its ad content repeatedly, only to receive the same rejection notices no matter what changes it made. The ads weren’t inflammatory. They were straightforward: “Turn Game Time into God Time,” “Christian Games for Kids,” “Safe Bible Games for Kids.”
Google’s policy supposedly prohibits “selecting an audience based on sensitive information, such as health information or religious beliefs.” But TruPlay wasn’t targeting a religious audience or harvesting private data. It was advertising Christian kids’ content to the general public.
Google’s response wasn’t “you’re targeting.” It was “your content is too sensitive to advertise.”
That’s the move. “Sensitive” once meant porn, violence, or content not suitable for children. Now it means “Christian games for kids.”
TikTok, the ACLJ says, applied the same logic with even less transparency. The platform allegedly suspended TruPlay’s advertising account over unspecified “repeated violations,” without explaining what those violations were. The ACLJ says one rejected ad contained the word “church.” Another issue allegedly involved an App Store preview image showing Jesus on the cross — not in the ad itself, but in the app’s images. The ACLJ claims TikTok barred advertising anyway.
RELATED: Google’s new plan: To learn everything about you from your online shopping
 Photo by Idrees MOHAMMED/AFP via Getty Images
Photo by Idrees MOHAMMED/AFP via Getty Images
You can’t fix what you’re not allowed to understand. That’s the point of opacity. You don’t get a rule you can follow. You get a verdict.
What makes this even more revealing is the economic angle. This isn’t Google or TikTok avoiding ads that risk scaring off customers. TruPlay offers the kind of content parents actively want. Platforms should want that money. Instead, they appear willing to lose revenue just to suppress anything overtly Christian and family-friendly.
The ACLJ has sent a letter to Rep. Jim Jordan (R-Ohio), chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, urging an investigation into what it calls “systemic discrimination” against Christian content creators and advertisers — part of a broader pattern of viewpoint-based censorship.
Google and TikTok will respond with the standard defense: We’re private companies. We can do what we want.
Fine. But stop pretending you’re Switzerland. If you present yourself as a neutral platform open to all, while quietly functioning as a political gatekeeper, you don’t get to hide behind the language of neutrality when people notice the double standard.
You can’t have it both ways. Either you’re Switzerland — or you’re not.
Google and TikTok are not. It’s time to treat them accordingly.
Conservatives can’t barbecue their way through national collapse

Conservatives want to be left alone. They have families, jobs, churches, hobbies. They love their country, but they stay busy and comfortable. Politics feels like something for other people — activists, ideologues, the perpetually aggrieved. The left may dream of tearing the system down in a fiery Marxist revolution, but one solid vote every couple of years or so should keep the crazies in check. Then it’s back to work, back to Little League, back to the barbecue.
That belief sustained many on the right for decades. It has become a liability.
A vote followed by retreat no longer suffices. Saving the country requires engagement, sacrifice, and the willingness to place political reality over personal comfort.
The sunshine conservative lives under the assumption that the American system more or less runs itself, that excesses can be corrected with minimal effort, and that power remains constrained by shared norms. Those assumptions no longer hold. The times that try men’s souls have returned, and the sunshine conservative is about to discover that comfort carries a cost.
For years, a bipartisan consensus reshaped the country through mass immigration. Call it conspiracy if you like, but incentives explain it better.
Democrats saw a reliable path to permanent power. Immigrants arrive without wealth, social capital, or political leverage. They gravitate toward the party that promises redistribution and protection. Every program — health care, housing, loans, benefits — tilts toward newcomers. Open borders grow government, entrench dependency, and expand the progressive patronage machine.
Republican incentives looked different but proved just as corrosive. Conservative voters opposed mass immigration, legal and illegal alike, but party leadership feared one thing above all else: being called racist.
Progressive programming successfully framed the idea of America as a homeland — run for the benefit of its people — as morally suspect. Any attempt to articulate national interest became “nativism.” Chamber of Commerce Republicans exploited that fear, importing millions of workers willing to accept suppressed wages while silencing critics through ritual denunciation.
While the country changed, conservatives largely stood aside. The transformation unsettled them, but lawn care got cheaper and food delivery faster. The sunshine conservative preferred comfort to confrontation. Political activism felt vulgar. Winners, after all, make money and buy boats.
Now the bill has come due.
Human trafficking. Drug flows. Violent crime. Overcrowded hospitals. Stagnant wages. Exploding housing costs. The social fabric frays under the weight of policies designed to benefit elites while disciplining everyone else.
RELATED: Aristotle’s ancient guide to tyranny reads like a modern manual
 Blaze Media Illustration
Blaze Media Illustration
The Trump administration’s effort to remove the worst offenders collides with a system addicted to inflow. Obvious solutions exist — employer enforcement, E-Verify, ending the H-1B visa scam, taxing remittances heavily — but those measures threaten donor interests. Instead, enforcement proceeds piecemeal, state by state, criminal by criminal.
Each attempt to exercise authority triggers panic among mainstream conservatives. They fret about optics. They warn about norms. They clutch abstractions while the left shoots at or runs over federal agents, storms churches, and treats public order as optional. Establishment voices agonize over power even as their opponents wield it without hesitation.
A friend of mine returned from the Global War on Terror with what doctors labeled post-traumatic stress disorder. The diagnosis missed the point. His trauma didn’t come from violence alone. It came from clarity. He had lived in a world where stakes mattered, where power operated openly, where failure carried consequences. Returning to a culture submerged in therapeutic language, pronouns, and safe spaces proved disorienting. Everyone else lived inside a fantasy and demanded that he play along.
Eventually, he learned to stay quiet. He still regards much of what surrounds him as childish and unmoored from reality.
That reaction mirrors what many feel toward sunshine conservatives. They cling to a story about politics that bears no resemblance to how power functions. When confronted with evidence, they demand that reality conform to their narrative. It never does. That narrative existed to pacify them, to make them manageable. They defend it with the same fervor with which the left defends its own delusions.
Each crisis cracks the façade. An assassination. A church invasion. A city surrendered to disorder. Every time, a few more conservatives wake up — only to be swarmed by those demanding a return to small talk about tax rates and process. The problem never lay with those who saw the danger. It lay with those insisting everyone else look away.
RELATED: The left’s ‘fascism’ routine is a permission slip for violence
 Blaze Media Illustration
Blaze Media Illustration
The question no longer concerns policy tweaks. It concerns survival. One side believes the country deserves preservation and repair. The other treats it as illegitimate and disposable. That divide cannot be bridged by nostalgia or proceduralism.
The sunshine conservative era has ended. Saving the country requires engagement, sacrifice, and the willingness to place political reality over personal comfort. It requires choosing the future of one’s children over quarterly returns. It requires the disciplined use of power to defend the nation’s institutions, borders, and communities — even when that makes polite society uncomfortable.
A vote followed by retreat no longer suffices. The fantasy that it does belongs with other comforting lies. The right can either shed it or be ruled by those who never believed it in the first place.
How the 30-year mortgage helped create a permanent housing bubble

You won’t hear many people object to President Trump’s executive order to ban corporate purchases of residential homes. The idea sounds like common sense. But it targets a minor symptom while leaving the real disease untouched — and in some respects, it risks making that disease worse.
Institutional home-buying already peaked during the COVID-era bubble and has receded since then. In most markets, corporate ownership represents a small share of total inventory. Even at its height, it never explained why housing costs exploded for everyone else. High prices created the opportunity for institutional buyers, not the other way around.
The goal should not be cheaper debt. It should be cheaper homes.
Government policy inflated the housing market. Institutional buyers simply responded.
During COVID, the Federal Reserve pushed interest rates toward zero. Mortgage rates fell below 3%. At the same time, the Fed bought roughly $2.7 trillion in mortgage-backed securities, and HUD expanded “affordable homeownership” programs that widened the pool of subsidized buyers. Those policies produced predictable results.
When the government offers 2.5% interest for 30 years — often paired with minimal down payments backed by the FHA — buyers flood the market. Sellers respond by raising prices. The bubble becomes a feature, not a bug.
Institutional buyers entered that environment because it looked like easy money. Higher home prices also pushed rents up, so developers built more homes for long-term rental. Both trends flowed from the same source: a government-shaped market that made housing unaffordable, then subsidized the unaffordability.
Trump now seems focused on the symptom — corporate buyers — while ignoring the machinery that inflated the market in the first place.
He has spent months fighting Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell to bring rates back down toward zero. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve still holds about $2.1 trillion in mortgage-backed securities. Trump has also announced a plan for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to purchase another $200 billion in MBS. The stated goal is to lower mortgage rates.
But the goal should not be cheaper debt. It should be cheaper homes.
 mphillips007 via iStock/Getty Images
mphillips007 via iStock/Getty Images
Artificially lowering rates props up prices and slows correction. Prices in many markets have begun to soften. That correction should continue. Policies designed to suppress rates will keep prices elevated and risk inflating the next bubble.
That brings us back to corporate home-buying. Even at the COVID peak, institutional buyers — defined as entities owning at least 100 single-family homes — owned about 3.1% of the housing stock. That number has since fallen to around 1%. Investors see the market turning, and they have started backing away.
So Trump’s corporate-purchase ban arrives late, targets a relatively small share of the market, and risks becoming cosmetic cover for policies that keep the bubble inflated.
If Trump wants to drive prices down and permanently realign housing with median incomes, he has to reverse the policies that inflated the bubble. That means attacking the structure, not the headline.
Get government out of the mortgage market. Trump’s next Federal Reserve chair must commit to unwinding the Fed’s mortgage-backed securities portfolio. That $2.1 trillion cushion keeps mortgage rates lower than the market would otherwise set. Those artificially low rates inflate home prices.
End universal “homeownership for everyone” policy. The federal government keeps subsidizing buyers who are not ready to buy. Those programs inject cash into housing demand that would not exist in a real market. The goal should align prices with income, not chase a utopian dream of universal ownership. After decades of subsidies, deductions, and federal credit support, the home ownership rate still sits around the mid-60% range.
Stop chasing near-zero interest rates. A 30-year loan at 2% sounds appealing until you realize what it does to prices. Cheap money bids up homes across the board. Buyers pay the price forever even as politicians brag about the “deal.” Trump should let the market set rates. Recent rate cuts have not restored normal home buying either. Sales remain weak because prices remain too high.
End the 30-year fixed mortgage. Instead of floating longer loans — 50 years? Madness! — the country should move in the opposite direction. Before the New Deal era, short-term mortgages, often three to seven years, dominated the market. Federal policy transformed that structure.
Franklin D. Roosevelt signed the National Housing Act of 1934, establishing the Federal Housing Authority. The FHA insured long-term, fully amortizing mortgages with fixed rates, low down payments, and standardized payment schedules. That system moved the market away from short-term balloon loans and laid the foundation for longer terms.
RELATED: America tried to save the planet and forgot to save itself
 jhorrocks via iStock/Getty Images
jhorrocks via iStock/Getty Images
Congress eventually authorized the 30-year mortgage in 1954. VA loans under the GI Bill and the expansion of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac later built a secondary market that made long-term fixed-rate loans attractive to lenders.
Government insurance, guarantees, and liquidity support made 30-year fixed mortgages feasible, which is why they represent 80%-90% of U.S. mortgages today. Without those interventions, lenders would not carry that risk.
The larger point remains simple: Sellers can’t charge prices buyers can’t pay. Prices explode only when government subsidies and government-backed long-term debt expand what buyers can “afford” on paper.
Unwind the subsidies. Unwind the guarantees. Unwind the cheap-money machinery. Let incomes, not federal policy, set the ceiling.
Housing should function like other consumer markets, not be engineered by Washington. Prices should reflect what people earn.
That’s the fix. Everything else treats symptoms and pretends to solve the problem.
Voters won’t buy ‘freedom in Iran’ while Minneapolis goes lawless

My buddy Ryan Rhodes, who’s running for Congress in Iowa’s 4th District, drove north to Minnesota to see the chaos in Minneapolis up close. What he found looked worse than the headlines.
“You have a really Islamo-communist set of people who we have imported” to this country, Rhodes told me. “I think you’ve got a lot of Muslim Brotherhood agents in there, people whose message is, ‘We have taken over this city.’ Forget just elections. We lose our country if we keep allowing these people to come in.”
Americans can handle hard truths. They can handle sacrifice. They can handle a fight. What they won’t handle is watching the bad guys win again.
Rhodes wasn’t talking like a guy chasing clicks. He sounded like a guy staring at the map and realizing tyranny doesn’t need a passport. It can sit three hours from your front door.
So forgive me if I don’t have much patience for the foreign-policy sermonizing right now. How am I supposed to sell voters on “freedom in Iran” while Minneapolis slides toward lawlessness and Washington keeps acting powerless to stop it?
That pitch collapses fast with working-class Americans, especially while the economy limps along and trust remains thin on the ground. Republican voters want competence, results, and consequences for people who harm the country. They want accountability at home first.
We’ve lived what happens without it.
COVID cracked Trump’s first term because bureaucrats and “experts” ran wild, issued edicts, trashed livelihoods, and faced zero consequences. Then the George Floyd riots poured gasoline on the fire. Cities burned while federal authorities watched the destruction unfold.
Trump’s comeback last year required more than winning an election. It required overcoming a full-scale assault on the country’s spirit — and on the right to live as free citizens. The machine didn’t just beat Republicans at the ballot box. It hunted them. Roughly 1,400 Americans were rounded up by the Biden regime over the January 6 “insurrection.” They went after Trump too. They went after anyone in their way.
Those four years didn’t just wreck careers in Washington. They reached down to the local level — school boards acting like petty dictators, public health officials issuing mask and jab mandates, and doctors’ offices turning into political compliance centers. Families paid the price.
Now the country watches the same disease spread again.
People see domestic radicals attack federal officers in the streets. They watch Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz (D) posture like a man protecting the mob, not the public. They hear Minneapolis leaders talk like ICE has no right to exist inside city limits. The footage looks like a warning, not an isolated event.
Remember CHAZ/CHOP in Seattle in 2020? That’s the template: Declare a zone off-limits to law, romanticize the lawlessness, and dare the state to reassert control. Every time the government blinks, the radicals learn the lesson: Push harder.
Demoralization has started to set in. I see it on Facebook and on the ground. In Iowa, I’m seeing campaign photos that would’ve been unthinkable in past cycles: small crowds, low energy, people staying home. Iowa has its first open Republican gubernatorial primary in 15 years, and the mood should feel electric. Instead, it feels like exhaustion.
As things stand, fewer Republicans will vote in the June primary than voted in the 2016 Iowa caucuses. That’s unheard of. Iowa has more than 700,000 registered Republicans. I wouldn’t bet on even 200,000 showing up.
That should terrify the White House.
RELATED: America now looks like a marriage headed for divorce — with no exit
 Photo by Madison Thorn/Anadolu via Getty Images
Photo by Madison Thorn/Anadolu via Getty Images
Trump isn’t on the ballot in Iowa anymore. He doesn’t need to win another primary. But the movement still needs to win elections. It needs to win them in places like Iowa — and it needs to win them while the country watches cities like Minneapolis drift toward foreign-flag politics and open contempt for American sovereignty.
Rhodes put it bluntly: If we don’t stop this, we’re watching an Islamic conquest play out in real time, one “sanctuary” city at a time. Great Britain didn’t fall in a day. It surrendered by degrees.
So what do voters need to see now?
Not another speech. Not another promise. Not another commission. Not another “investigation” that ends in a shrug.
They need to see what they were promised when Trump ran for a second term: accountability.
If the country watches Minnesota slide into open defiance of federal law and nobody pays a price for it, voters will conclude the system can’t defend them. And if the system can’t defend them at home, it has no credibility abroad.
Start with Minnesota. Make it plain that “no-go zones” don’t exist in the United States. Enforce the law. Protect federal agents. Prosecute the people who assault them. Strip federal money from jurisdictions that obstruct enforcement. Treat organized lawlessness like organized lawlessness, not a political disagreement.
Americans can handle hard truths. They can handle sacrifice. They can handle a fight.
What they won’t handle is watching the bad guys win again — without consequences.
America now looks like a marriage headed for divorce — with no exit
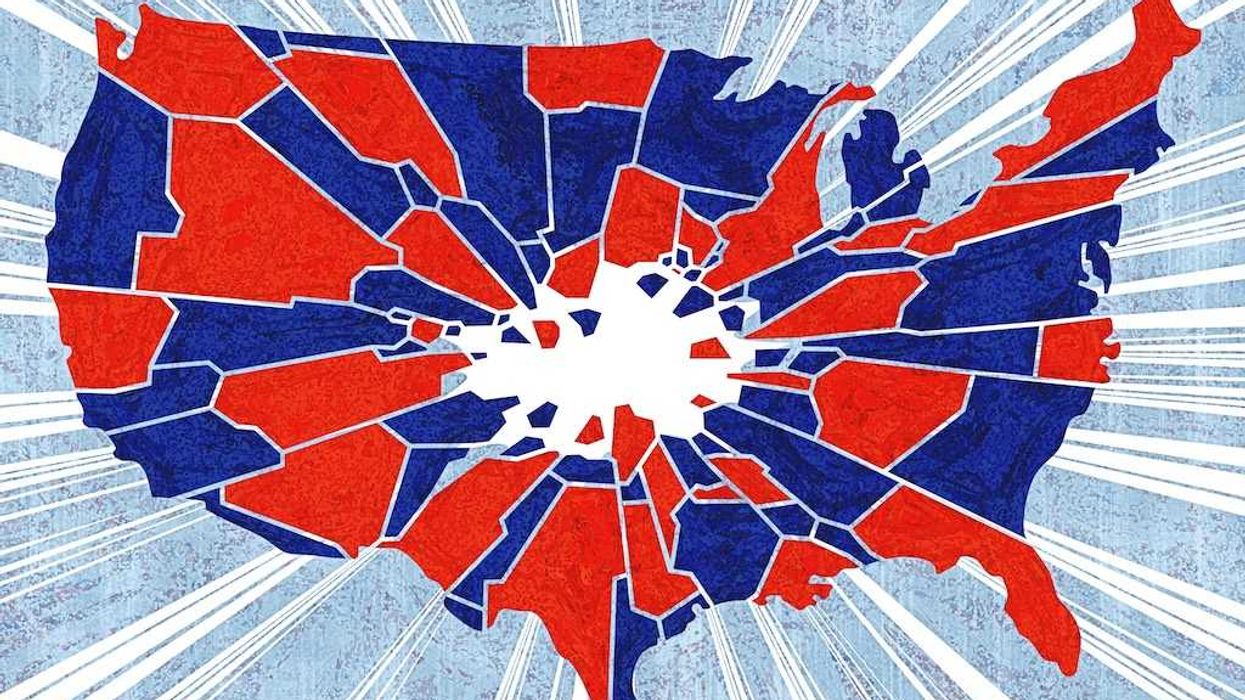
Marriages rarely end over one argument. They fall apart through a long breakdown in communication, a growing inability to resolve disagreements, and the slow realization that two people no longer walk toward the same future.
Healthy marriages don’t require full agreement on every subject. They require compromise on the decisions that shape daily life: money, children, priorities, responsibilities. They also require shared goals.
No tidy divorce court exists for a nation-state. We share one flag, one legal framework, and one public square.
When those goals diverge — and neither side will realign — the relationship becomes unsustainable. The law calls the condition “irreconcilable differences.”
America now lives in that condition.
We remain bound under one nation, one Constitution, and one civic home. But we no longer share a common purpose. We no longer share a common story about what the country is, why it exists, or whether it deserves to endure.
This conflict no longer turns on tax rates or regulatory policy. It turns on the legitimacy and direction of the American experiment itself.
The modern left no longer argues about how to preserve the American system. It treats the system as the problem. Democratic leaders and activists call for “fundamental transformation,” flirt with socialism, and talk about the founding less as a flawed but noble legacy than as a moral failure that demands replacement. In that worldview, America doesn’t need reform. America needs erasure.
The right still believes the country can be repaired and preserved. The left increasingly treats the country as something to dismantle.
This rupture shows up in concrete ways. In 2021, the National Archives placed a “harmful language” warning on the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence — the documents that define the nation. That doesn’t signal ordinary partisan dispute. It signals contempt for the country’s moral foundation.
Socialism sits at the center of this divide. It contradicts the American system at its roots. America rests on the premise that rights come from God, not government. Socialism elevates the state over the individual and makes rights conditional on political approval. It centralizes power in the name of enforced equality — “equity.”
RELATED: Americans aren’t arguing any more — we’re speaking different languages
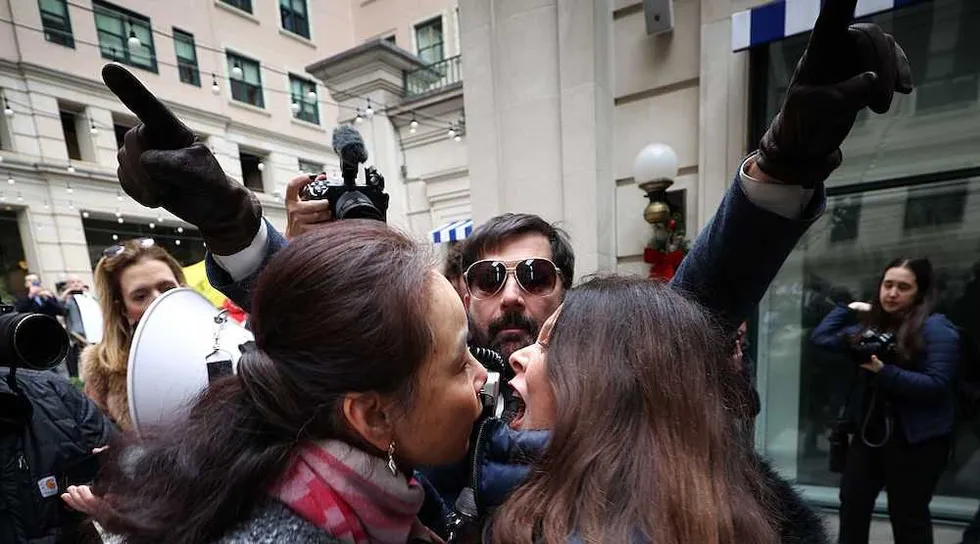 Photo by Win McNamee/Getty Images
Photo by Win McNamee/Getty Images
America protects private property as an extension of liberty. It channels ambition into innovation and prosperity. Socialism treats success as a social offense and demands equality of outcome. When people refuse to surrender the fruits of their labor, socialism turns to coercion. Coercion requires centralized authority. Centralized authority punishes dissent.
The pattern repeats: less freedom, greater dependency, and a governing model incompatible with constitutional self-rule.
The irony remains hard to miss. The left calls Donald Trump “Hitler” while cheering figures like New York City Mayor Zohran Mamdani, an avowed socialist. Yet the Nazi Party sold itself as the National Socialist German Workers’ Party — a collectivist project built on centralized power and state control.
The same left often excuses Antifa, a movement built on intimidation, street violence, and political enforcement designed to silence opposition. Those tactics don’t belong to liberal democracy. They belong to regimes that fear debate.
Even basic reality has become contested. The left and right can’t agree on something as elemental as what a man or a woman is. The Supreme Court recently showcased the collapse when ACLU attorneys arguing sex-based discrimination refused to define “woman.” When a society refuses to name biological facts that every civilization once treated as obvious, compromise collapses with it.
This crisis goes deeper than polarization. It reaches the level of knowledge itself. The left increasingly treats biology, history, and moral limits as malleable social constructs. The right still believes objective reality binds us all.
These aren’t normal disagreements. They describe incompatible worldviews. And incompatibility carries consequences.
During the COVID era, polls found majorities of Democrats willing to endorse coercive measures against the unvaccinated, including house arrest. Nearly half supported imprisoning people who questioned vaccine efficacy. Those numbers didn’t represent a fringe. They revealed a growing comfort with state force in service of ideological conformity.
After Trump’s 2016 election, many friendships survived political conflict. By 2020, after years of dehumanization — after constant accusations of “Nazism” aimed at ordinary voters — many of those relationships broke. The political battle stopped sounding like disagreement and started sounding like moral extermination.
RELATED: Washington, DC, has become a hostile city-state
 Photo by Astrid Riecken For The Washington Post via Getty Images
Photo by Astrid Riecken For The Washington Post via Getty Images
In September 2025, someone assassinated Charlie Kirk. Large segments of the left didn’t just rationalize the killing. Many celebrated it.
After Scott Adams died following a long fight with cancer, prominent voices responded with mockery instead of decency. People magazine ran a headline labeling him “disgraced.” Even death became a political verdict.
This is what irreconcilable differences look like at a national scale.
A country cannot endure when one side believes the nation stands as fundamentally good — worthy of preservation and reform — while the other believes it stands as irredeemably evil and must be dismantled. Marriages end when partners stop seeing each other as allies and start treating each other as enemies.
Nations fracture for the same reason.
America cannot solve this the way a couple dissolves a marriage. The Constitution binds us to one civic order. No clean separation awaits. No tidy divorce court exists for a nation-state. We share one flag, one legal framework, and one public square.
When irreconcilable differences exist but separation remains impossible, the danger grows.
Only three paths remain: recommitment to constitutional principles, enforced coexistence through expanding coercion, or escalation into open conflict as dehumanization becomes normal.
Pretending this amounts to another election cycle, another policy dispute, or another cable-news food fight invites catastrophe. A nation cannot survive when its people no longer agree on what it is, why it exists, or whether it deserves to continue.
Unlike a failed marriage, America can’t walk away.
Blaze Media • Don lemon • First Amendment • Freedom of religion • Freedom of speech • Opinion & analysis
A protest doesn’t become lawful because Don Lemon livestreams it

What should have been a peaceful Sunday service at Cities Church in St. Paul, Minnesota, turned into a political ambush. Roughly 30 anti-ICE protesters pushed into the sanctuary mid-worship, chanting slogans and confronting church leaders as families tried to pray.
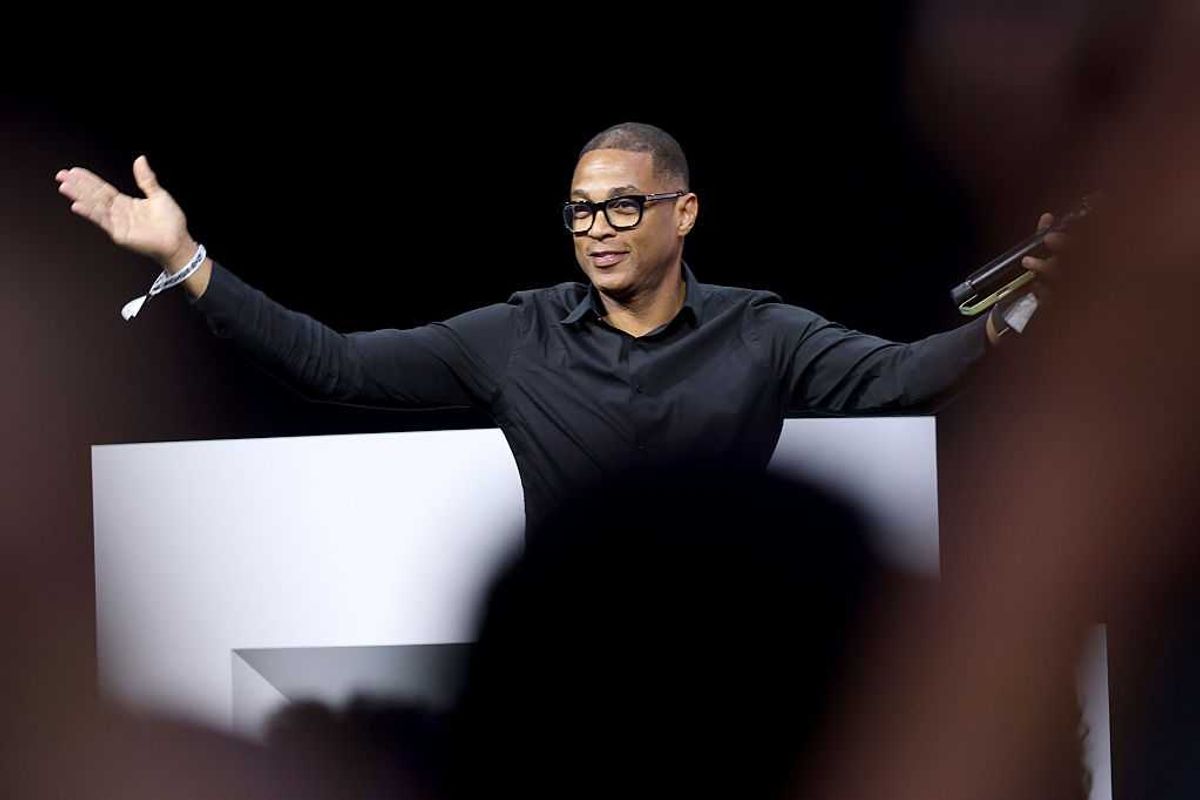
Disgraced former CNN anchor Don Lemon was there, too, livestreaming the chaos.
If activists can storm a church mid-service, scream at families, and then hide behind the First Amendment, the standard becomes simple: The loudest mob sets the rules.
The Department of Justice has opened a formal investigation and signaled that federal protections for houses of worship may apply. Assistant Attorney General Harmeet Dhillon noted on the “Glenn Beck Program” that the activists’ conduct could implicate the Freedom of Access to Clinic Entrances Act, which bars intimidation, obstruction, and interference with the free exercise of religion in places of worship. The protesters may have also violated the Ku Klux Klan Act, a post-Civil War law that makes it illegal to terrorize and violate the civil rights of citizens.
According to multiple reports, the demonstrators were tied to the Racial Justice Network and aimed their protest at a church leader they accused of working with Immigration and Customs Enforcement. The protest followed rising tensions in Minnesota after the fatal shooting of anti-ICE activist Renee Nicole Good during a confrontation with federal agents.
Lemon framed the entire spectacle as civic virtue. He insisted he was “not an activist, but a journalist” and argued that protest inside a church remains constitutionally protected speech.
The footage tells a messier story.
Video released after the incident shows Lemon interacting with the group beforehand, appearing familiar with organizers and the plan. One outlet described the operation as “Operation Pull-Up.” That undercuts the narrative Lemon later pushed — that he simply arrived to document an event that unexpectedly “spilled” into a worship service.
Intent matters. So does outcome. The outcome looked like this: a sanctuary overrun, a service derailed, congregants shaken, and children crying while activists shouted and gestured at the pews.
That is far from “peaceful assembly.” It is targeted disruption.
The First Amendment protects speech. It does not grant a roaming license to invade private spaces and commandeer them for political theater. Rights have edges because other people have rights too. Worshippers do not lose their liberty because activists feel righteous.
That basic distinction keeps a free society from collapsing into a contest of intimidation.
RELATED: Americans aren’t arguing any more — we’re speaking different languages
 Photo by Heather Diehl/Getty Images
Photo by Heather Diehl/Getty Images
This case matters because it tests whether the country still draws that line. If activists can storm a church mid-service, scream at families, and then hide behind the First Amendment, the standard becomes simple: The loudest mob sets the rules. Next week it will be another church. Then a synagogue. Then any gathering that activists decide deserves punishment.
The Justice Department is right to examine the FACE Act here. Congress passed it to stop coercion dressed up as protest — the use of obstruction and intimidation to prevent Americans from exercising basic freedoms. That principle doesn’t change because the target shifts from an abortion clinic to a church sanctuary.
The press corps’ selective outrage makes the problem worse. Cultural elites demand “safety” and “inclusion” in every other arena, but many of them treat Christian worship as an acceptable target. They police speech in classrooms and boardrooms, then shrug when activists shout down prayer.
That double standard signals something deeper than hypocrisy. It signals permission.
Lemon’s defense captured the rot in one sentence: Making people uncomfortable, he said, is “what protests are about.” Fine. Protest often makes people uncomfortable. But discomfort does not justify trespass. It does not excuse intimidation. It does not cancel someone else’s right to worship in peace.
A society that cannot protect sacred spaces will not protect much else for long. If the law refuses to punish conduct like this, the lesson will spread fast: Invade, disrupt, harass — then claim virtue and dare anyone to stop you.
America does not need a new normal where mobs treat churches like political stages. It needs consequences.
Blaze Media • Ice raids • Immigration and customs enforcement • Minneapolis • Minnesota • Opinion & analysis
The left’s ‘fascism’ routine is a permission slip for violence
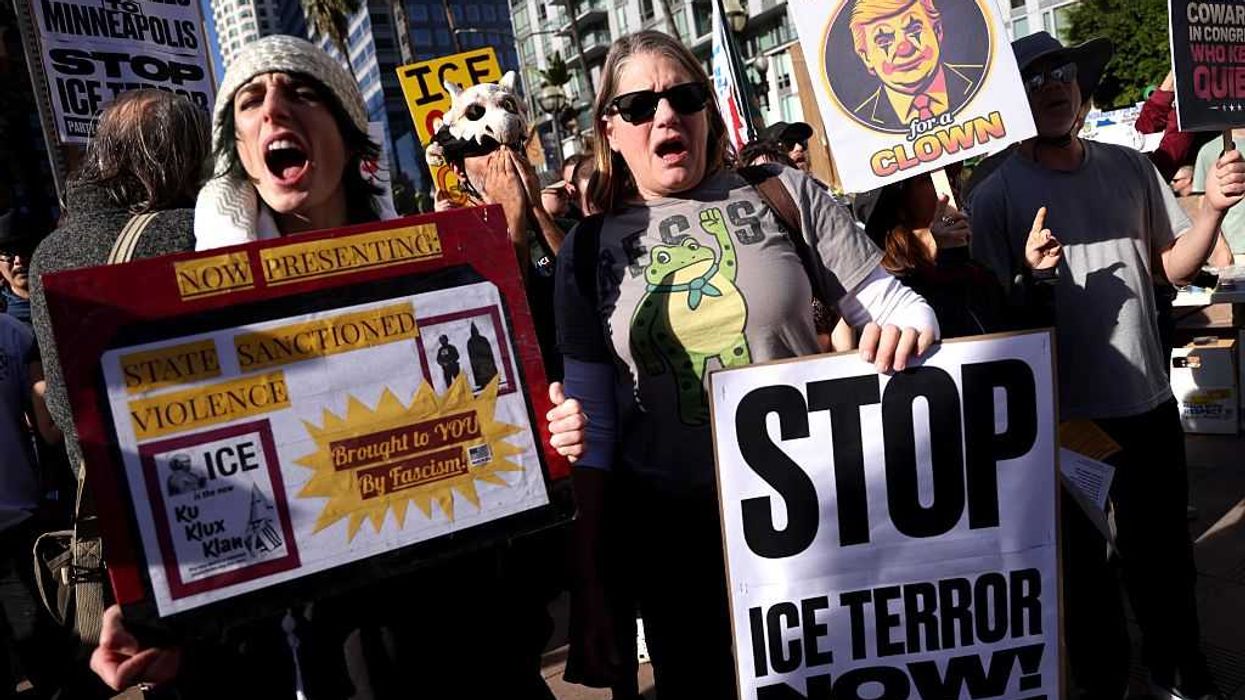

The alternate reality Democrats have constructed is falling apart in real time. Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.) said the following when asked to comment on an Immigration and Customs Enforcement agent shooting a woman in Minneapolis who was attempting to run over the agent with her car: “What we saw today was a criminal, a criminal, murder a woman and shoot her in the head while she was trying to escape and flee for her life.”
She then called “disgusting” the “editorializing” of those who argue that the ICE agent was in front of the car as it was accelerating, just before he fired. “Watch it for yourself, watch it for yourself,” she concluded, with supreme confidence that any viewer would see with the same skew of her own lens.
A significant portion of the American media and popular culture has normalized the idea that totalitarians have taken over the government.
Minneapolis Mayor Jacob Frey (D) went even harder over the rhetorical cliff in responding to the shooting. He classified interpretations of the ICE officer’s action as self-defense as “bull***t” and demanded that ICE “get the f**k out of Minneapolis.” Mayor Zohran Mamdani (D) in New York followed suit, calling the event a “murder” and a “horror.”
It is a stark bit of evidence of how American society has been warped by the twisted rhetoric of the radical left regarding political conflict in our country.
The video from the officer who fired at the vehicle indicates clearly, however, that it was accelerating in his direction, with him close enough to touch the hood. How is it possible to watch video footage and see it as the “murder” of someone “flee[ing] for her life”? The vehicle was illegally blocking a law enforcement vehicle. Instead of complying with the demand to exit the vehicle as any sane person would do, the driver hit the gas, making contact with the law enforcement officer before being shot.
Are we to believe that ICE agents came there precisely to kill her?
The New York Times published a video analysis that supposedly debunks the claim that the agent fired in self-defense. How? Well, the wheels of the SUV turned to the right just in time to avoid hitting the agent. Never mind that the agent was standing just in front of the vehicle when it started to move forward quickly, and he moved to avoid it. By the Times’ logic, the agent would apparently have been justified to use force only after the SUV had hit him.
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz (D) said he doubts an FBI investigation of the shooting could reach a “fair outcome.” He’s given no reason why he believes this. But of course, if your view is that all sides not directly aligned with you ideologically are Nazis, this is a logical conclusion.
One might first hypothesize that Ocasio-Cortez, Frey, Walz, Mamdani, and others who share their bizarre interpretation of the evidence are cognitively challenged in some way. We do not wholly discount this possibility.
But the more likely answer is that such things become possible when a significant portion of the American media and popular culture has normalized the idea that totalitarians have taken over the government and are actively looking to kill their opponents. In such a scenario, attempting to run over the totalitarians with your car might not only be an acceptable choice — it might be the most moral one.
The Department of Homeland Security Assistant Secretary Tricia McLaughlin connected the event to the language the far left has been using to describe ICE: “This is the direct consequence of constant attacks and demonization of our officers by sanctuary politicians who fuel and encourage rampant assaults on our law enforcement who are facing [a] 1,300% increase in assaults against them and an 8,000% increase in death threats.”
There is no doubt that political radicals have been foaming at the mouth about ICE and other aspects of the Trump administration’s policies in the most extremist language. They’ve justified using violence against them even since before the first Trump administration took office.
RELATED: Fraud thrived under Democrats’ no-questions-asked rule
 Photo by Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images
Photo by Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images
The alleged assassin who murdered Charlie Kirk in September, who was involved in a relationship with a transsexual, had come to believe that Kirk and other conservatives who criticized the overreach of trans radical activism were such a deadly threat that only lethal force was appropriate. He wrote anti-fascist messages on the casings of the bullets he used.
None of this is a surprise in a culture in which American nationalism is seen as the equivalent of Nazism and violent attacks against the Trump administration and its supporters are cheered on and encouraged. And it is not just the explicitly political media that embraces this insanity.
Witness the response to “One Battle After Another,” the recent film by Paul Thomas Anderson, loosely based on Thomas Pynchon’s novel “Vineland.” Starring Leonardo DiCaprio and Sean Penn, the film cheerleads for a radical anti-fascist terrorist organization as they wage war on American police and immigration forces. Penn is cast in a stupendously comical role as a caricature of which the left never tires: He is a military figure and a white supremacist who nonetheless is sexually attracted to nonwhites. All of the admirable figures in the film are revolutionary terrorists. The response by critics in the mainstream media has been a virtually unanimous cheer.
We are in a dangerous place. Leftist radicals are giving no indication of cooling their rhetoric — or their actions.
Buckle up. It is going to get rougher before it gets better.
Editor’s note: This article appeared originally at the American Mind.
When human worth becomes conditional, caregiving becomes impossible

Most people can care for an ill or disabled loved one for a week on compassion alone. Some can do it for a month. A few can make it a year or two.
But when care stretches into decades, compassion stops carrying the load. Emotion fades. Circumstances grind. What remains isn’t how someone feels about a life. What remains is whether they believe that life still matters.
When a culture treats reality as optional, action becomes dangerous and courage looks reckless. Without shared moral ground, bravery itself becomes suspect.
Caregiving strips life down to essentials. It forces a question our culture prefers to keep abstract: Why does this life still have value when it costs so much to sustain it?
C.S. Lewis warned that a society cannot survive if it mocks virtue while demanding its fruits. In “The Abolition of Man,” he described “men without chests” — people trained to think and desire but not to stand. Without a formed moral center, courage collapses. Duty feels suspect. Endurance looks irrational.
Caregivers learn this in a harsh classroom.
You cannot sustain decades of care if human worth is negotiable. You cannot rise day after day to guard the vulnerable if life’s value depends on productivity, independence, improvement, or the absence of suffering. Long care requires stewardship — the conviction that a life has been entrusted to us, not evaluated by us.
I once met a man who told me he was dating a woman in a wheelchair. He spoke with genuine enthusiasm about how good it made him feel to do everything for her. He sounded animated, even proud. He talked at length about his experience, his emotions, the satisfaction he drew from being needed.
He said very little about her.
I asked how long they’d been dating.
“Two weeks,” he said, beaming.
I smiled wearily and told him, “Get back to me in two decades.”
Care that depends on how it makes us feel rarely survives once feeling fades. What endures over decades isn’t the satisfaction of being needed. It’s settled clarity about the worth of the person being cared for, independent of what the caregiver receives in return.
RELATED: Christian, what do you believe when faith stops being theoretical?
 ImagineGolf via iStock/Getty Images
ImagineGolf via iStock/Getty Images
In that man’s excitement, everything centered on his emotions. What was missing was any recognition of her value apart from her condition — or apart from what caring for her did for him.
I didn’t hear, “I’m dating a woman,” or “I’ve met someone extraordinary.” I heard, again and again, “I’m dating a woman in a wheelchair.” The chair became the headline, not the person. He might as well have celebrated the better parking.
She had become useful to him. That’s not the same thing as being valued.
This way of thinking doesn’t stay confined to personal relationships. It scales.
The public reckoning surrounding Daniel Penny exposed it. He acted to protect others he believed were in danger — not because it felt good but because action was required. That kind of clarity now unsettles a society more comfortable with sentiment than obligation.
We claim we want people to intervene, to protect others, to act decisively when danger appears. Then someone does, and we hesitate. We second-guess. We prosecute. We distance ourselves.
We want courage but not conviction.
Lewis wouldn’t be surprised. When a culture treats reality as optional, action becomes dangerous and courage looks reckless. Responsibility suddenly feels threatening. Without shared moral ground, bravery itself becomes suspect.
Francis Schaeffer traced the path forward from that confusion. Once a culture detaches human worth from anything objective, it stops honoring life and starts managing it. Value becomes conditional. And conditions always change.
That logic now shows itself in plain view. When Gov. Kathy Hochul (D-N.Y.) pushes to legalize medical aid in dying in New York, the same fracture appears. We punish those who act as though life must be defended, while elevating leaders who treat life as something to administer and conclude.
Those aren’t separate debates. They’re the same belief, applied differently.
If life holds value only when it functions well, caregiving becomes irrational. If worth depends on autonomy, dependence becomes disposable. If suffering disqualifies, endurance becomes foolish.
And yet caregivers endure.
RELATED: Caregiving decisions begin in the bathroom
 MTStock Studio via iStock/Getty Images
MTStock Studio via iStock/Getty Images
That clarity came back to me during a conversation on my radio show. A man described a brief illness his wife had suffered. The house fell apart. Meals became takeout. Work got missed. Romance disappeared. He sounded exhausted just recalling it.
“What carried you through?” I asked.
He paused. “I guess … love.”
“How long did this last?” I said.
“Five days.”
“I guess … love” carried him through five days.
Uncertainty can survive a week. It cannot sustain 14,000 days.
He wasn’t wrong though. Love matters. But love that sustains five days must anchor itself in something deeper to sustain 40 years.
Caregivers may begin with compassion. They endure with conviction.
A life doesn’t become less valuable because it becomes harder to carry.
Caregiving isn’t a special category of moral life. It is a concentrated version of the human condition. What sustains caregivers over time is what sustains courage, faithfulness, and duty anywhere else.
Lewis reminded us that our feelings don’t create value. They respond to it. When we reverse that order, we don’t become more compassionate. We lose our bearings.
Treating human worth as conditional may flatter our emotions. It may even make us feel noble. But it trains us to prize how we feel over the people entrusted to our care.
Over time, that trade leaves us prosecuting men like Daniel Penny while electing leaders like Kathy Hochul.
It might soothe the heart for a moment.
It cannot sustain a society.
search
calander
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||
categories
Archives
navigation
Recent posts
- Gavin Newsom Laughs Off Potential Face-Off With Kamala In 2028: ‘That’s Fate’ If It Happens February 23, 2026
- Trump Says Netflix Should Fire ‘Racist, Trump Deranged’ Susan Rice February 23, 2026
- Americans Asked To ‘Shelter In Place’ As Cartel-Related Violence Spills Into Mexican Tourist Hubs February 23, 2026
- Chaos Erupts In Mexico After Cartel Boss ‘El Mencho’ Killed By Special Forces February 23, 2026
- First Snow Arrives With Blizzard Set To Drop Feet Of Snow On Northeast February 23, 2026
- Chronological Snobs and the Founding Fathers February 23, 2026
- Remembering Bill Mazeroski and Baseball’s Biggest Home Run February 23, 2026






